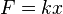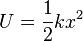Hooke's law facts for kids

Hooke's Law is an important rule in physics and mechanics. It was discovered by a scientist named Robert Hooke.
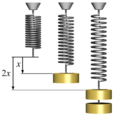
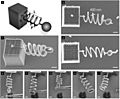
This law helps us understand how things stretch or squish, like a spring. It says that if you pull or push a spring, the amount it stretches or squishes is directly related to how much force you use. Imagine pulling a spring twice as hard; it will stretch twice as much!
This rule works for many materials, but only up to a certain point called the elastic limit. If you pull or push too hard, the material might break or stay stretched forever. Materials that follow Hooke's Law are called "Hookean" materials.
Contents
Understanding the Spring Equation
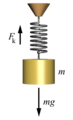
When you push or pull a spring, its length changes by a certain amount. We can describe this change using a simple equation:
Let's break down what these letters mean:
- F is the force you apply to the spring. This is how hard you push or pull it.
- k is a special number called the spring constant. It tells you how stiff the spring is. A higher 'k' means a stiffer spring.
- x is the distance the spring was stretched or squished from its normal resting position.
When 'x' is zero, it means the spring is at its normal length, not stretched or squished at all. This is called the equilibrium position.
This equation works best for a linear spring. A linear spring is one that is only being pushed or pulled in a straight line, like up and down or side to side.
What is Elastic Potential Energy?
Many everyday things store energy because they are stretched, squished, twisted, or bent. This stored energy is called elastic potential energy.
Think about these examples:
- A stretched rubber band
- A spring in a toy
- Bungee cords
- The shock absorbers in a car
When you stretch or squish something, you put energy into it. This energy doesn't disappear; it's saved inside the object. For example, when you pull back the string of a bow to shoot an arrow, you store elastic potential energy in the bow. When you let go, this stored energy quickly changes into kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion, and the arrow flies away!
The equation for elastic potential energy is:
Here's what the letters mean:
- U is the elastic potential energy stored in the object.
- k is the spring constant, just like in the spring equation. It tells us how stiff the spring or elastic material is.
- x is the distance the object was stretched or squished from its normal position.
Images for kids
-
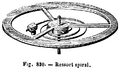
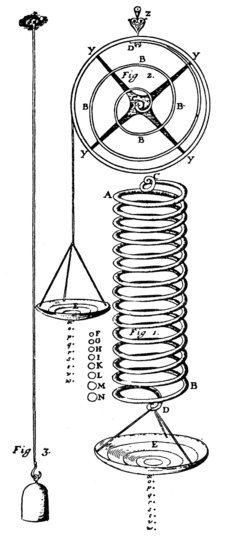
Bourdon tubes use Hooke's law to measure gas pressure. The force from the pressure unwinds the coiled tube, and the amount it unwinds shows the pressure.
See also
 In Spanish: Ley de elasticidad de Hooke para niños
In Spanish: Ley de elasticidad de Hooke para niños
 | Precious Adams |
 | Lauren Anderson |
 | Janet Collins |