Equilibrium facts for kids
An equilibrium is a special state where everything is perfectly balanced and stable. Imagine a tug-of-war where both teams are pulling with the exact same strength – nothing moves! That's equilibrium. When a system is in equilibrium, it doesn't change on its own. This idea is used in many different areas of study.
- Hydrostatic equilibrium happens when liquids are still and balanced, like water in a calm lake.
- Thermal equilibrium means an object is the same temperature as its surroundings. No heat is moving in or out.
- Homeostasis is how living things keep their inside conditions steady. For example, your body works hard to keep your temperature just right.
- Equilibrioception is your sense of balance. It helps you stand or walk without falling over.
Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium describes what happens in chemical reactions over time. Think of it like a two-way street for chemicals. In many reactions, chemicals combine to form new ones (the forward reaction). But sometimes, the new chemicals can also change back into the original ones (the backward reaction).
When a reaction reaches equilibrium, the amounts of the starting chemicals (reactants) and the new chemicals (products) stop changing. It doesn't mean the reaction has stopped! It means the forward reaction and the backward reaction are happening at the same speed. So, the amounts of chemicals stay constant.
For example, imagine a reaction like this:  The double arrow (
The double arrow (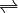 ) is super important! It shows that the reaction can go both ways. This balance between the forward and backward reactions leads to something called the equilibrium constant.
) is super important! It shows that the reaction can go both ways. This balance between the forward and backward reactions leads to something called the equilibrium constant.
What is the Equilibrium Constant?
The equilibrium constant, often written as Kc, is a number that tells us the ratio of products to reactants when a reaction is at equilibrium. It helps chemists understand how much of the starting chemicals will turn into products.
The formula for the equilibrium constant looks a bit complex, but it's just a ratio: 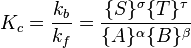 Basically, it compares the amounts of products to the amounts of reactants, with each amount raised to a certain power based on the reaction.
Basically, it compares the amounts of products to the amounts of reactants, with each amount raised to a certain power based on the reaction.
- If Kc is a very large number, it means that at equilibrium, there are mostly products. Almost all the starting chemicals have turned into new ones. Burning paper is an example – it turns almost completely into ash and smoke.
- If Kc is a very small number, it means there are mostly reactants. Very little of the starting chemicals turn into products.
- If Kc is close to 1, you'll find a good mix of both products and reactants when the reaction is balanced.
Chemists often say reactions with large Kc values are "favorable." This just means they tend to make a lot of products. Reactions with small Kc values are "unfavorable," meaning they don't make many products. But remember, "unfavorable" doesn't mean useless! Some very important reactions have small Kc values, like making ammonia gas for fertilizers (Haber process).
Understanding the equilibrium constant helps chemists predict how much product they can get from a reaction. It's like knowing the recipe for a cake – it tells you how much of each ingredient you'll end up with.
Le Chatelier's Principle
 Le Chatelier's principle is a super helpful rule for predicting how an equilibrium will react to changes. It says that if you change something in a system at equilibrium, the system will try to counteract that change. It's like a seesaw trying to get back to level!
Le Chatelier's principle is a super helpful rule for predicting how an equilibrium will react to changes. It says that if you change something in a system at equilibrium, the system will try to counteract that change. It's like a seesaw trying to get back to level!
For example, if you add more of a starting chemical to a reaction at equilibrium, the system will try to use up that extra chemical. It will shift the equilibrium to make more products. If you remove a product, the system will try to make more of it to replace what's gone. This principle helps chemists control reactions to get more of the products they want.
See also
In Spanish: Equilibrium para niños

