Hurricane Juan (1985) facts for kids
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS/NWS) | |

Hurricane Juan near peak intensity
|
|
| Formed | October 26, 1985 |
|---|---|
| Dissipated | November 1, 1985 |
| Highest winds | 1-minute sustained: 85 mph (140 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 971 mbar (hPa); 28.67 inHg |
| Fatalities | 24 direct, 50 indirect |
| Damage | $2.8 billion (1985 USD) (Includes indirect losses) |
| Areas affected | Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, Florida Panhandle |
| Part of the 1985 Atlantic hurricane season | |
Hurricane Juan in 1985 was a very costly storm during the 1985 hurricane season. Even though it was not the strongest hurricane, it caused a lot of damage, about $1.5 billion. It also led to the deaths of about 24 people directly and 50 indirectly. Despite the severe impact, the name Juan was not removed from the list of hurricane names.
Contents
Understanding Hurricanes
Hurricanes are huge, spinning storms that form over warm ocean waters. They bring very strong winds, heavy rain, and big waves called storm surges. Scientists use a scale to measure how strong a hurricane is. This scale goes from Category 1 (the weakest) to Category 5 (the strongest).
How Hurricanes Form
Hurricanes start when warm, moist air rises from the ocean. This creates an area of low pressure. More air rushes in to fill this space, and the Earth's spin makes the air swirl. As the storm grows, it picks up more energy from the warm water. This makes the winds stronger and the storm bigger.
Hurricane Categories Explained
- Category 1: Winds from 74 to 95 miles per hour. Can cause some damage to homes and power lines.
- Category 2: Winds from 96 to 110 miles per hour. Can cause more damage, like breaking windows and uprooting trees.
- Category 3: Winds from 111 to 129 miles per hour. Can cause major damage to buildings and widespread power outages.
- Category 4: Winds from 130 to 156 miles per hour. Can cause extreme damage, making many areas unlivable.
- Category 5: Winds 157 miles per hour or higher. Causes catastrophic damage, destroying many homes and buildings.
Hurricane Juan's Journey
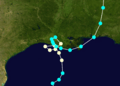
Hurricane Juan began forming on October 26, 1985. It started in the Gulf of Mexico and slowly moved towards the United States. Juan was a Category 1 hurricane, which is the lowest category. However, it was still a very dangerous storm.
Juan's Path and Landfall
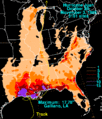
The hurricane moved slowly, which made its impact worse. It spent a long time over the same areas, bringing continuous heavy rain and strong winds. Juan made landfall, meaning it hit the coast, in Louisiana. After hitting Louisiana, it continued to affect other states.
States Affected by Juan
Hurricane Juan brought its strong winds and heavy rains to several states. The areas most affected included:
The Impact of Hurricane Juan
Even as a Category 1 hurricane, Juan caused a lot of problems. The slow movement of the storm meant that rain fell for a long time. This led to severe flooding in many places. The strong winds also knocked down trees and power lines.
Damage and Costs
The total damage from Hurricane Juan was estimated at about $1.5 billion. This included damage to homes, businesses, and farms. Roads were flooded, and many people lost electricity. The cost was very high for a storm of its strength.
Lives Lost
Sadly, Hurricane Juan also led to the loss of life. About 24 people died directly because of the storm. Another 50 people died indirectly, meaning their deaths were related to the storm's effects, like accidents during cleanup.
Why Was Juan's Name Not Retired?
After a hurricane causes a lot of damage or deaths, its name is usually "retired." This means the name is removed from the list of hurricane names. This is done to honor the victims and to avoid using a name associated with such a terrible event again. For example, Hurricane Katrina's name was retired.
However, despite the high cost and fatalities, the name Juan was not retired in 1986. This was unusual because many other storms with less damage have had their names retired. The decision to retire a name is made by a special committee. Sometimes, names are not retired if the damage is seen as less severe than other storms, or if the storm's impact was spread out over a wide area rather than concentrated in one spot.
Images for kids