Texas night snake facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Texas night snake |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Colubridae |
| Genus: | Hypsiglena |
| Species: |
H. jani
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hypsiglena jani (Dugès, 1865)
|
|
 |
|
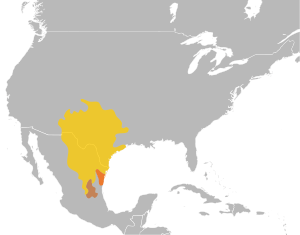
| The distribution of Hypsiglena jani (brown), which now includes the two former subspecies Hypsiglena torquata dunklei (orange), and Hypsiglena torquata texana (yellow). | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Texas night snake or Chihuahuan night snake (scientific name: Hypsiglena jani) is a small snake. It belongs to the Colubridae family. This snake is found in the southwestern United States and nearby parts of northeastern Mexico. It is a little bit venomous, but it's not dangerous to people.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The scientific name jani was given to this snake to honor an Italian scientist named Giorgio Jan. He was a taxonomist, which means he studied how to classify living things.
How to Spot a Texas Night Snake
The Texas night snake is usually about 10 to 16 inches (25 to 41 centimetres) long. The longest one ever found was about 20 inches (51 cm).
It is often light gray or tan in color. It has dark brown or dark gray spots along its back. Its belly is usually plain with no markings.
This snake has smooth scales on its back. Its eyes have pupils that look like a thin line, similar to a cat's eye. The Texas night snake has fangs at the back of its mouth. It is considered venomous, but its venom is not harmful to humans.
Nighttime Habits
As its name suggests, the Texas night snake is a nocturnal animal. This means it is most active at night.
What Do They Eat?
The Texas night snake mainly eats lizards. It will also sometimes eat smaller snakes. Occasionally, it might eat soft-bodied insects too.
Where They Live
These snakes like dry areas with rocky ground. They prefer habitats that are semi-arid, meaning they don't get a lot of rain.
Reproduction
The Texas night snake lays eggs. This means it is an oviparous species. They usually breed during the spring rainy season.
A female snake will lay about 4 to 6 eggs. These eggs take about 8 weeks to hatch. The eggs are usually about 27 mm (1.1 in) long and 10 mm (3⁄8 in) wide. When the baby snakes hatch, they are about 15 cm (5.9 in) long.
Where They Are Found
The Texas night snake lives in a wide area. You can find them from southern Kansas down to southern Colorado. They also live throughout New Mexico and the western part of Texas. Their range extends south into central Mexico.
Different Types of Texas Night Snakes
Scientists recognize three different types, or subspecies, of the Texas night snake. These are like different versions of the same snake.
- Hypsiglena jani dunklei Taylor, 1938
- Hypsiglena jani jani (Dugès, 1865)
- Hypsiglena jani texana Stejneger, 1893
Species Hypsiglena jani at The Reptile Database

