Incilius macrocristatus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Incilius macrocristatus |
|
|---|---|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Bufonidae |
| Genus: | Incilius |
| Species: |
I. macrocristatus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Incilius macrocristatus Firschein and Smith, 1957
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Bufo valliceps macrocristatus Firschein and Smith, 1957 |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Incilius macrocristatus is a special kind of toad that used to be called Bufo macrocristatus. Its common name is the large-crested toad or huge-crested toad. This toad belongs to the Bufonidae family, which includes many different types of toads. It's a rare animal, meaning there aren't many of them left in the wild.
Contents
Where Does the Large-Crested Toad Live?
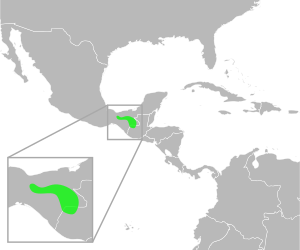
This unique toad makes its home in specific parts of North America. You can find it in Chiapas, which is a state in southern Mexico. It also lives in the country right next door, Guatemala.
Natural Homes of the Toad
The large-crested toad prefers certain types of natural habitats. These include:
- Cloud forests: These are misty, humid forests found in mountains. They often have clouds that hang low, keeping the trees and ground very wet.
- Pine-oak-Liquidambar forests: These are forests where you'll find a mix of pine trees, oak trees, and a tree called Liquidambar. This type of forest also provides the right conditions for the toad to thrive.
Life Cycle and Reproduction
Like many amphibians, the large-crested toad needs water to lay its eggs and for its young to grow.
Breeding in Streams
When it's time to have babies, these toads go to streams. This is where they breed, meaning the adult toads mate and lay their eggs in the water. The young toads, called tadpoles, will then grow and develop in these streams before they are ready to live on land.
Why Is This Toad in Danger?
The large-crested toad is considered a rare species, and its numbers are shrinking. This means it's facing threats that could make it disappear forever if we don't protect it.
Threats to Its Habitat
The main reason this toad is in danger is habitat loss. This happens when the places where the toad lives are destroyed or changed.
- Agriculture: People often clear forests to create land for farming. This takes away the toad's home.
- Human settlement: As more people build houses and towns, they also take over the toad's natural living spaces.
- Water pollution: The streams and water sources that the toads use for breeding can become dirty. This pollution comes from things like chemicals used in farming or waste from human settlements. Dirty water makes it hard for the toads and their young to survive.
Protecting these special toads means protecting their forests and keeping their water clean.
See also
 In Spanish: Incilius macrocristatus para niños
In Spanish: Incilius macrocristatus para niños
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |


