Induction coil facts for kids
An induction coil (sometimes called a "spark coil") is a special electrical device. It works like a transformer, which means it can change electricity from one level to another. An induction coil takes a low-voltage direct current (DC) – like from a battery – and turns it into very high-voltage pulses. Imagine a quick, powerful zap of electricity!
To make these high-voltage zaps, the coil needs to quickly turn the low-voltage electricity on and off. It does this with a vibrating switch called an interrupter. This quick on-off action creates the strong electrical changes needed to make the high voltage.
Contents
How Induction Coils Work
An induction coil has two main parts: a primary coil and a secondary coil. Both are made of wire wrapped around an iron core.
Creating High Voltage
When a low-voltage direct current (DC) flows into the primary coil, it creates a magnetic field. To get a high voltage in the secondary coil, this magnetic field needs to change very quickly. The induction coil uses a special part called an interrupter to do this.
The interrupter acts like a fast-moving switch. It repeatedly breaks the flow of electricity in the primary coil. This rapid turning on and off makes the magnetic field around the coils change very fast. This quick change then "induces" (or creates) a much higher voltage in the secondary coil. This process is based on Faraday's law of induction, a key rule in physics.
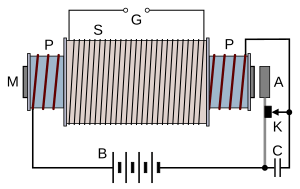
Parts of an Induction Coil
Here are the main parts you would find in a typical induction coil:
- A = Armature (a moving part of the interrupter)
- B = Battery (provides the low-voltage direct current)
- C = Capacitor (helps the coil work more efficiently)
- G = Spark gap (where the high-voltage spark appears)
- K = Interrupter (the vibrating switch that turns the current on and off)
- M = Iron core (the central part around which the coils are wrapped)
- P = Primary coil (the first coil, connected to the low-voltage supply)
- S = Secondary coil (the second coil, where the high voltage is produced)
History and Uses
The induction coil was the very first type of transformer ever invented. It was a very important invention in the 1800s and early 1900s.
Past Uses
From the 1880s to the 1920s, induction coils were used in many different ways:
- X-ray machines: They helped power early X-ray devices, allowing doctors to see inside the body.
- Radio transmitters: They were used in early radio transmitters to create the sparks needed for sending radio signals.
- Arc lighting: Some early electric lights, called arc lights, used induction coils.
- Medical devices: They were even found in some unusual medical devices that people used a long time ago.
Modern Uses
Today, induction coils are not as common as they once were, but they are still very important in one key area:
- Ignition coils: Almost every internal combustion engine (like those in cars and motorcycles) uses an ignition coil. This is a type of induction coil that creates the high-voltage spark needed to ignite the fuel in the engine.
- Physics education: Induction coils are also used in schools and universities to teach students about how electricity and magnetism work together.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bobina de inducción para niños
In Spanish: Bobina de inducción para niños
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |