Kanji bush facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Kanji bush |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| A. inaequilatera, in flower. | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Clade: | Mimosoideae |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: |
A. inaequilatera
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia inaequilatera Domin
|
|
 |
|
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Acacia inaequilatera, commonly known as kanji bush, is a unique tree found in Australia. It's also called baderi, camel bush, fire wattle, kanyji bush, or ranji bush. This tree belongs to the Mimosaceae family.
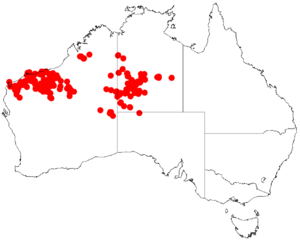
You can find the kanji bush mostly in the dry, semi-arid areas of Western Australia and the Northern Territory. It often grows where a type of grass called spinifex is common.
Contents
What is Kanji Bush Like?
The kanji bush is a twisted or "gnarled" tree or shrub. It usually has one main trunk and rough, corky bark. Its leaves and stems are spiny.
Size and Bark
This plant typically grows between 2 to 5 meters tall. Sometimes, it can even reach up to 8 meters! The main trunk has thick, rough, dark grey to black bark. This bark is often marked by fires, showing how tough the tree is.
Leaves and Flowers
Like most Acacia species, the kanji bush doesn't have true leaves. Instead, it has special leaf-like structures called phyllodes. These phyllodes are blue-grey and have a curved middle vein. Each one ends in a sharp, needle-like tip. You'll also notice a pair of curved spines at the base of each phyllode. They are tough and leathery, shaped like an oval but uneven, ranging from 1.5 to 7 cm long.
The flowers of the kanji bush are quite special. Unlike many Acacia plants that have pure yellow flowers, these are yellow with a reddish-purple center. They grow in round clusters, about 5 mm across. You can see these flowers between May and October.
Pods and Seeds
After flowering, the kanji bush produces flat, curved pods. These pods can be up to 10 cm long and 1 cm wide. They might be strongly curved or even coiled! When they are young, the pods are a pale maroon color. As they get older, they turn a mid-brown or pinkish-purplish brown.
Inside the pods are dull, dark brown seeds. Each seed is about 4 to 6 mm long and shaped like a small oval or sphere.
Life Cycle and Fire
The kanji bush is very good at surviving fires. It can quickly grow back after a bushfire, either from its base or from special buds under its bark. However, it doesn't live very long, usually less than ten years.
How Kanji Bush Got Its Name
The kanji bush was first officially described by a botanist named Karel Domin in 1926. It was later given a different scientific name, Racosperma inaequilaterum, but then changed back to Acacia in 2006.
The second part of its scientific name, inaequilatera, comes from a Latin word meaning "with unequal sides." This refers to its very unevenly shaped phyllodes. The kanji bush is related to Acacia trudgeniana and sometimes looks similar to Acacia marramamba and Acacia pyrifolia.
Where Kanji Bush Grows
The kanji bush is found in scattered areas across the dry parts of Australia. You can see it in the northwestern tip of South Australia, the southwestern parts of the Northern Territory, and the Pilbara and southern Kimberley regions of Western Australia.
It likes to grow on rocky hillsides, stony hills, and plains. It prefers sandy to loamy soils that have a lot of stones. Often, it's part of tall shrubland areas where spinifex grass grows underneath.
Uses of Kanji Bush
Indigenous Australian people have traditionally used the kanji bush for many purposes.
Food and Drink
The seeds of the kanji bush were an important food source. They could be eaten raw, roasted over a fire, or ground into a flour. This flour was then used to make damper, a type of bread. The ground seeds could also be used to make a drink that tasted a bit like coffee.
Acacia seeds are very nutritious! They contain about 26% protein, 26% carbohydrates, 32% fiber, and 9% fat. The tree also produces an edible gum that oozes from its trunk and branches.
Medicine
The bark of the kanji bush was used for medicinal purposes. It could be boiled in water or burned to ash, then applied to treat skin problems and sores. The bark also contains substances called tannins. When soaked in water, these tannins create a solution that was used to treat diarrhoea and dysentery.
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |




