Kavalactone facts for kids
Kavalactones are natural compounds found mainly in the roots of the kava plant. You can also find them in a plant called Shell ginger (Alpinia zerumbet). Scientists are studying kavalactones to see if they can have effects like helping people feel calm or sleepy. They are being researched for their potential to act as anxiolytic (calming) and sedative (sleep-inducing) substances.
Contents
How Kavalactones Work
Kavalactones are being studied for how they affect the body. Some early research suggests they might interact with certain body processes. For example, they could affect how your body handles other medicines. This is because they might influence special proteins called enzymes in your liver. These enzymes help break down many things, including medicines.
Research on Kavalactones
Many studies are looking into the possible effects of kava and its kavalactones. Researchers want to understand if kavalactones can truly help with anxiety. They are also studying any possible side effects, like how kava might affect the liver. It's important to know that kava contains many different compounds, and scientists are still figuring out which ones cause specific effects.
Some research also suggests that kavalactone-like compounds might help protect cells. This could be useful against damage caused by high glucose (sugar) levels.
Important Safety Information
It's important to know that some kavalactones can affect enzymes in your body. These enzymes are involved in how your body processes different substances.
In a small number of people, using kava, especially strong extracts, has been linked to hepatotoxicity. This means it could cause damage to the liver. This happened more often with kava extracts than with traditional kava root powders. Always be careful and seek advice from an adult or doctor if you have questions about any plant-based products.
Different Kavalactone Types
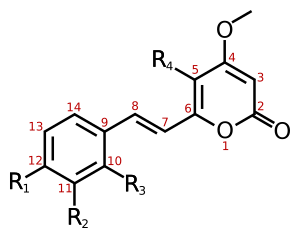
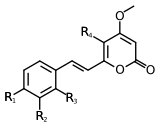
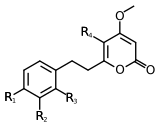
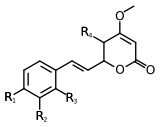
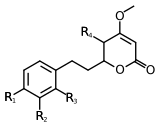
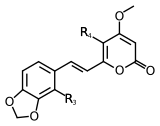
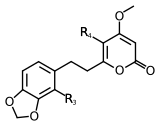
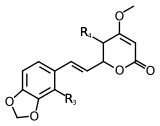
Scientists have found at least 18 different types of kavalactones. One of the first ones discovered was called methysticin. There are also many similar compounds. Some kavalactones have a special ring shape called an alpha-pyrone. Others are slightly different in their chemical structure.
Once kavalactones are in your body, they usually stay for about 9 hours before your body starts to get rid of them.
 | Jewel Prestage |
 | Ella Baker |
 | Fannie Lou Hamer |