Keiō facts for kids
The Keiō (pronounced "Kay-oh") was a special time period in Japanese history, known as a nengō (which means "year name"). It came after the Genji era and just before the famous Meiji era. This period lasted from April 1865 to September 1868. During these years, Japan had two emperors: Emperor Kōmei and his son, Emperor Meiji. The name Keiō itself means "Joyous Concord," which suggests a time of peace and agreement, even though it was a period of big changes.
Important Events of the Keiō Era
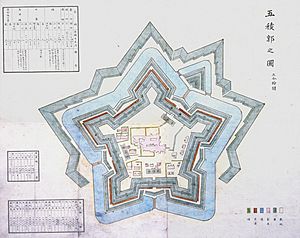
- 1866 (Keiō 2): Construction began on the Goryōkaku star-shaped fort in Hakodate. This was an important military fort.
- September 28, 1866 (Keiō 2): Tokugawa Iemochi, who was the shogun (the military ruler of Japan), passed away in Osaka. After his death, Tokugawa Yoshinobu was chosen to become the new shogun.
- January 10, 1867 (Keiō 2): Yoshinobu officially became the shogun in a formal ceremony.
- January 30, 1867 (Keiō 2): Emperor Kōmei passed away. His son, who would become Emperor Meiji, then took his place in a process called senso, which means the transfer of the emperor's role.
- November 10, 1867 (Keiō 3): An important announcement from the Imperial court declared that the emperor's government would be restored. This meant the emperor would regain more power, moving away from the shogun's rule.
- 1868 (Keiō 4): The Boshin War began with the Battle of Toba-Fushimi. This was a civil war between supporters of the Imperial court and those who supported the shogun.
- September 3, 1868 (Keiō 4): The city of Edo, which was the shogun's capital, was renamed "Tokyo." This new name means "Eastern Capital."
- October 8, 1868 (Keiō 4): The Battle of Aizu began. This was another major battle during the Boshin War.
- October 12, 1868 (Keiō 4): Emperor Meiji's role as the monarch (the head of the country) was officially confirmed through special ceremonies called sokui.
- October 23, 1868 (Keiō 4): The era name was formally changed from Keiō to Meiji. At this time, a general amnesty was also given, which meant many people involved in the recent conflicts were forgiven.
In 1868, the emperor moved his Imperial court from Kyoto to Tokyo. Edo Castle, which used to be the shogun's home, became an Imperial palace. This move officially made Tokyo the new capital of Japan.
Keio University is a famous school in Japan that was named after this era. It is one of the oldest universities in the country.
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Keiō para niños
In Spanish: Keiō para niños
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |