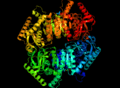Lactate dehydrogenase facts for kids
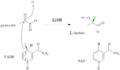
Lactate dehydrogenase, often called LDH, is a special helper molecule known as an enzyme. You can find LDH in almost every living cell, whether it's in animals, plants, or tiny prokaryotes (like bacteria). Its main job is to help change one chemical, called lactate, into another, called pyruvic acid, and then back again.
What LDH Does
LDH plays a very important role in your body, especially when your muscles are working hard. When you exercise intensely, your muscles can build up a lot of lactic acid. If too much lactic acid builds up, your muscles can get tired and stop working well. LDH helps to prevent this by managing the lactic acid levels. It helps your muscles keep working without getting too tired.
How LDH is Built
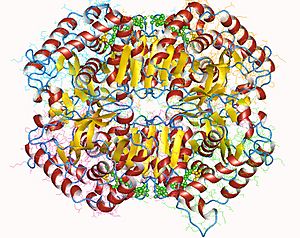
Each LDH molecule is made up of four smaller parts, like building blocks. These parts are called subunits. There are slightly different types of LDH found in different parts of your body. For example, the main type of LDH found in your lungs has two 'M' subunits and two 'H' subunits (written as 2H2M).
The 'M' and 'H' subunits are created from instructions found in different genes. The 'M' subunit's instructions come from a gene called LDHA, which is located on human chromosome 11. The 'H' subunit's instructions come from a gene called LDHB, found on human chromosome 12.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Lactato deshidrogenasa para niños
In Spanish: Lactato deshidrogenasa para niños