Laguña Creek facts for kids
Laguña Creek is a stream in the state of Arizona, in the southwestern United States. It flows through Navajo and Apache Counties. This creek was also known as Tyende Creek in the past. Laguña Creek is an important waterway in the dry landscape of the Colorado Plateau.
Contents
Where Laguña Creek Starts and Ends
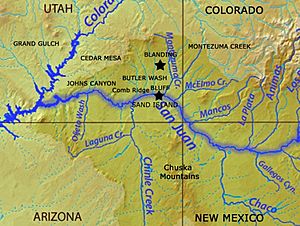
Laguña Creek begins high up in the mountains. Its starting point, called its source, is where two smaller canyons meet. These are Long Canyon and Dowozhiebito Canyon. This meeting point is at the head of Tsegi Canyon, about 6,325 feet (1,928 meters) above sea level.
The creek then flows downhill. Its ending point, called its mouth, is in the Chinle Valley. Here, Laguña Creek joins with Chinle Wash. When these two streams come together, they form a larger stream called Chinle Creek. This happens at a lower elevation of about 4,774 feet (1,455 meters).
Laguña Creek's Journey to the Ocean
Chinle Creek, which is formed by Laguña Creek and Chinle Wash, is a tributary of the San Juan River. A tributary is a smaller stream or river that flows into a larger one. So, Chinle Creek flows into the San Juan River.
The San Juan River is also a tributary. It flows into the mighty Colorado River. The Colorado River is one of the longest rivers in North America. It travels through many states and even into Mexico before reaching the Gulf of California, which is part of the Pacific Ocean. This means that water from Laguña Creek eventually makes its way all the way to the ocean!
The Importance of Laguña Creek
Creeks like Laguña Creek are very important, especially in dry areas like Arizona. They provide water for plants, animals, and people. The water helps keep the land green and supports different kinds of wildlife.
Geography of the Area
Laguña Creek flows through a region known as the Colorado Plateau. This area is famous for its amazing landscapes. It has deep canyons, tall mesas (flat-topped hills), and unique rock formations. The water from creeks helps to shape these landscapes over many years.