Liberal arts education facts for kids
Liberal arts education is a traditional way of learning in Western higher education. The term "liberal arts" comes from Latin words meaning "free" (liberalis) and "skill" or "practice" (ars). It's about learning a wide range of subjects, not just one specific job skill. This type of education is different from training for a specific job, a profession, or a religious career.
The idea of "liberal arts" for learning goes back to ancient times, but its meaning has changed a lot. In ancient and medieval times, it included seven subjects. These were split into two groups: the trivium (grammar, logic, and rhetoric) and the quadrivium (astronomy, mathematics, geometry, and music). Today, "liberal arts" usually means studying many different subjects, like natural sciences, math, social sciences, arts, and humanities.
Contents
History of Liberal Arts Education
The idea of liberal arts began in Ancient Greece. Thinkers like Pythagoras believed the universe had a mathematical and geometric order. His followers connected astronomy, mathematics, geometry, and music into one area of study, which later became the "quadrivium." In ancient Athens, public speaking (rhetoric) was very important. This led to rhetoric, grammar, and logic becoming the "trivium." Together, these were known as the seven liberal arts.
Originally, these skills were thought to be essential for a free person to take part in public life. This included speaking in debates, defending oneself in court, and serving in the military. During the Middle Ages, schools usually taught the trivium first, followed by the quadrivium.
The term "liberal arts" (artes liberales in Latin) was used in formal education during the Roman Empire. The Roman writer Marcus Tullius Cicero might have been the first to use the term. Later, in the 5th century, Martianus Capella wrote a famous book that described the seven liberal arts as bridesmaids at a wedding, which helped make them a standard group of subjects.
The four "scientific" arts – music, arithmetic, geometry, and astronomy – were called the quadrivium. The other three "humanities" arts – grammar, logic, and rhetoric – were called the trivium. These two groups were studied in medieval universities. Over time, logic became very important in the trivium.
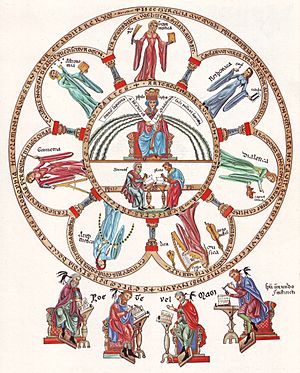
In the 12th century, a nun named Herrad of Landsberg created a famous image called Philosophy and the Seven Liberal Arts. It showed how learning and knowledge were organized around philosophy, like a beautiful rosette window in a cathedral. This image was part of an encyclopedia meant to teach women in the abbey.
During the Renaissance, thinkers in Italy and other parts of Europe changed the focus. They renamed the old trivium "Studia humanitatis" (humanities studies) and added history, Greek, and moral philosophy (ethics), with a new focus on poetry. This new way of learning spread across Europe and became the basis for educating leaders, government workers, religious figures, and professionals like lawyers and doctors.
The idea of a liberal arts education, based on classical languages and literature, lasted in Europe until the mid-20th century. In the United States, it faced challenges from academics who wanted to focus more on natural and social sciences.
A German scholar named Wilhelm von Humboldt also promoted an educational model that went beyond just job training. He believed that everyone needed a general understanding and a certain way of thinking to be good citizens, no matter their job. He wrote that if this basic education is provided, job skills are easy to learn later.
What Are Modern Liberal Arts?
Today, the term liberal arts covers four main areas:
- Natural Sciences: Like biology (the study of living things), physics (the study of matter and energy), chemistry (the study of substances), and astronomy (the study of space).
- Formal Sciences: Such as logic, mathematics, statistics, and computer science.
- Social Sciences: Including anthropology (the study of human societies), economics (the study of how societies use resources), psychology (the study of the mind), and sociology (the study of human behavior in groups).
- Arts and Humanities: This includes philosophy (the study of knowledge and existence), history, literature, music, and fine arts.
For example, many university programs in liberal arts include courses in philosophy, history, art, literature, and social sciences.
Liberal Arts in Secondary School
Liberal arts education at the high school level helps students get ready for college or university.
The subjects taught can be different from school to school, but they usually include:
- Languages (like English and foreign languages)
- Science (chemistry, biology)
- Geography
- Art and music
- Mathematics
- History
- Philosophy
- Civics (the study of citizens' rights and duties)
- Social sciences
Liberal Arts in the United States
In the United States, liberal arts colleges are schools that focus on undergraduate (first degree) studies in the liberal arts. Classes are often small, and professors usually focus more on teaching than on research.
Many four-year colleges also offer liberal arts degrees, and students studying other subjects can take liberal arts courses to get a broad education.
Traditionally, a bachelor's degree in liberal arts takes four years of full-time study. Some universities now offer a two-year associate degree in liberal arts. After finishing an undergraduate degree, students might go on to a graduate school for liberal arts or a professional school (like law or medicine).
Great Books Movement
In 1937, St. John's College changed its curriculum to focus on the Great Books of the Western World. This was a new type of education that aimed to be different from the increasingly specialized studies at other universities.
Liberal Arts in Europe
In many parts of Europe, liberal arts education has deep roots. In Germany and Austria, it's called humanistische Bildung (humanistic education). Schools called Gymnasium (like high schools) aim to give students a wide-ranging education to help them develop their personality and intellectual skills.
Because students in these schools often get a broad liberal arts education, universities in Europe sometimes have less focus on liberal arts in their first-degree programs compared to the US. Students are expected to use the skills they learned in high school to continue developing themselves through activities like music clubs or theater groups.
However, in recent years, some European universities have started to offer specific "liberal arts colleges" or programs, similar to the US model. Examples include Leiden University College The Hague and University College Utrecht in the Netherlands, and Bard College Berlin in Germany.
In England, universities like Winchester, University College London, and King's College London have launched modern liberal arts programs. In Scotland, the four-year undergraduate degree often includes a broad range of subjects in the first two years before students choose a specialty.
Liberal Arts in Asia
In the Philippines, all higher education institutions must include liberal arts subjects like history, art, and ethics in their general education curriculum. Jesuit universities, such as Ateneo de Manila University, have a strong liberal arts core that includes philosophy, theology, literature, and social sciences.
Many institutions in India also offer liberal arts degrees, including FLAME University and Ashoka University. Lingnan University in Hong Kong and International Christian University in Tokyo are also examples of liberal arts universities in Asia. Fulbright University Vietnam is the first liberal arts institution in Vietnam.
Liberal Arts in Australia
Campion College in Sydney is a Roman Catholic liberal arts college, founded in 2006. It offers a Bachelor of Arts in the Liberal Arts, focusing on history, literature, philosophy, and theology.
The Millis Institute in Brisbane also offers a Bachelor of Arts in the Liberal Arts. Recently, the University of Wollongong started a new "Western Civilisation" course, focusing on classic Western literature and art. Other universities like the University of Sydney and the University of Notre Dame Australia have also developed liberal arts courses.
See also
 In Spanish: Artes liberales para niños
In Spanish: Artes liberales para niños
- Bachelor of Liberal Arts
- Classical education
- Humanities
- Liberal arts college
- Liberal education