Lucerne Lake (California) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Lucerne Lake |
|
|---|---|
| Location | Mojave Desert San Bernardino County, California |
| Coordinates | 34°30′15″N 116°57′15″W / 34.5041°N 116.9542°W |
| Lake type | Endorheic basin |
| Primary outflows | Terminal (evaporation) |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 6 km (3.7 mi) |
| Max. width | 8 km (5.0 mi) |
| Shore length1 | 25 km (16 mi) |
| Surface elevation | 869 m (2,851 ft) |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
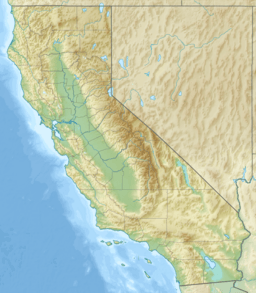
Lucerne Lake is a fascinating place in the Mojave Desert of San Bernardino County, California. It's not a lake with water all the time, but rather a dry lake bed. This means it's a flat area that used to be a lake, but now it's mostly dry.
Lucerne Lake is about 24 km (15 mi) east of Apple Valley. The dry lake bed is quite large, stretching about 6 km (3.7 mi) long and 8 km (5.0 mi) at its widest point. It's a unique part of the desert landscape.
Contents
What is a Dry Lake?
A dry lake, also known as a playa (pronounced PLY-uh), is a basin or depression that once held water. Over time, the water either evaporated or drained away. Lucerne Lake is a great example of this natural process.
Why Do Lakes Become Dry?
Lakes can become dry for several reasons. In places like the Mojave Desert, there isn't much rainfall. The sun is also very strong, causing water to evaporate quickly. Lucerne Lake is part of an Endorheic basin. This means it's a closed system where water flows in but doesn't flow out to rivers or oceans. Instead, any water that enters the basin stays there until it evaporates.
The Role of Evaporation
Evaporation is the main reason Lucerne Lake is dry. When water evaporates, it turns into vapor and goes into the air. This leaves behind any minerals or salts that were dissolved in the water. Over many years, this process can create a flat, salty surface on the lake bed.
Life in the Mojave Desert
Even though Lucerne Lake is dry, the surrounding Mojave Desert is home to many interesting plants and animals. They have special ways to survive in this harsh environment.
Desert Plants
Plants in the Mojave Desert are tough! They have adapted to live with very little water. Some common plants you might see near Lucerne Lake include:
- Creosote bush: This plant has waxy leaves that help it save water. It also smells like rain!
- Joshua tree: These iconic trees are a type of yucca. They grow slowly and can live for hundreds of years.
- Cacti: Many types of cacti, like the cholla and prickly pear, store water in their thick stems.
Desert Animals
Animals in the desert are often active at night when it's cooler. They also have special adaptations to find water and stay cool.
- Desert tortoise: This reptile can live a long time and digs burrows to escape the heat.
- Coyotes: These clever animals are common in the desert and hunt small prey.
- Roadrunners: Famous for their speed, these birds can run faster than they fly.
- Kangaroo rats: These small rodents can get all the water they need from the seeds they eat.
What Happens at a Dry Lake?
Dry lake beds like Lucerne Lake are very flat and open. This makes them useful for certain activities.
Land Speed Records
Because they are so flat, some dry lake beds are used for trying to set land speed records. People race special vehicles to see how fast they can go. While Lucerne Lake isn't as famous for this as some other dry lakes, its flat surface makes it suitable for such activities.
Filming and Recreation
The unique landscape of dry lakes is often used for filming movies, TV shows, and commercials. Their wide-open spaces and distinct look make them perfect backdrops. People also enjoy off-roading or flying model airplanes on these flat surfaces.
History of the Area
The area around Lucerne Lake has a long history.
Native American Presence
Long ago, Native American tribes lived in the Mojave Desert. They were very skilled at finding water and food in this challenging environment. They used resources from the land and traded with other groups.
Early Settlers
Later, explorers and settlers came to the area. They often used dry lake beds as natural pathways because they were so flat. The history of Lucerne Valley, the nearby community, is tied to these early developments.