Medieval Warm Period facts for kids
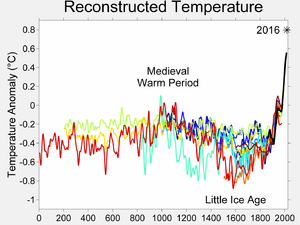
The Medieval Warm Period (MWP) was a time when parts of the Earth, especially the North Atlantic region, became unusually warm. This period lasted for about 400 years, from the 10th century to the 14th century. People often talk about this time when they discuss global warming today.
Some experts call it the Medieval Climatic Anomaly. This name helps us remember that it wasn't just about temperature. Other climate changes also happened during this period.
Contents
What Was the Medieval Warm Period?
The Medieval Warm Period, sometimes called the Medieval Climate Optimum, was a time of warmer temperatures in many parts of the world. It was most noticeable in the North Atlantic region. This period happened before the Little Ice Age, which was a cooler time.
Scientists study this period to understand how Earth's climate can change naturally. It helps them compare past climate shifts with the changes we see today.
When Did the Warm Period Happen?
This warmer time generally began around the year 950 AD. It continued until about 1250 AD. However, the exact start and end dates can vary a bit depending on the region. For example, some areas might have felt the warmth earlier or later.
This period covers parts of the 10th, 11th, 12th, 13th, and 14th centuries. It was a significant time for human history and the environment.
How Do We Know About Past Climates?
Scientists use many clues to figure out what the climate was like long ago. They look at things like:
- Ice cores: These are long tubes of ice drilled from glaciers. They contain trapped air bubbles and dust that show past temperatures and atmospheric conditions.
- Tree rings: The rings inside trees grow differently depending on the climate. Wide rings mean good growing conditions, often warmer and wetter.
- Lake sediments: Layers of mud and plant remains at the bottom of lakes can tell us about past rainfall and temperatures.
- Historical records: Old writings, like farming records or ship logs, sometimes mention weather conditions.
These clues help scientists build a picture of Earth's past climate.
Why Was This Period Important?
The Medieval Warm Period had a big impact on human societies. Warmer temperatures often meant better conditions for farming in some areas. This led to more food and growing populations.
For example, the Norse people, also known as Vikings, were able to settle in Greenland during this time. They farmed and raised livestock there. This would have been much harder during colder periods.
What Happened in Greenland?
During the Medieval Warm Period, the Norse settled in Greenland. They built farms and churches, like the Hvalsey Church. This church is now the best-preserved Norse ruin in Greenland. The warmer climate allowed them to grow crops and keep animals.
However, as the climate started to cool down again, especially with the start of the Little Ice Age, life became much harder for the Norse settlers. The last written records of them in Greenland are from 1408.
How Does It Compare to Today's Climate?
The Medieval Warm Period was a natural climate event. It was caused by things like changes in the sun's activity or volcanic eruptions. It was not caused by human activities like burning fossil fuels.
Today's global warming is different. Scientists agree that the current warming trend is mostly caused by human activities. These activities release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The current warming is also happening much faster and is more widespread than the Medieval Warm Period.
Studying past warm periods helps scientists understand how Earth's climate system works. It gives them valuable information to predict future climate changes.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Período cálido medieval para niños
In Spanish: Período cálido medieval para niños