Membrane protein facts for kids
A membrane protein is a special kind of protein that is attached to or goes through the outer layer of a cell or an organelle (which are like tiny organs inside a cell). Think of them as important workers stuck in the cell's walls.
These proteins are super important! About 20-30% of all the instructions (called genes) in your body's cells are for making membrane proteins. Many modern medicines work by targeting these proteins to help treat diseases.
Contents
What Membrane Proteins Do
Membrane proteins have many vital jobs that help living things survive:
Sending Messages
- Receptor proteins are like antennas. They pick up signals from outside the cell and pass the message inside. This helps cells know what's happening around them and react.
Moving Things Around
- Transport proteins are like tiny gates or pumps. They help move different molecules and ions (tiny charged particles) in and out of the cell. This is how cells get nutrients and get rid of waste.
Helping Chemical Reactions
- Enzyme proteins act like tiny helpers that speed up important chemical reactions. Many of these enzymes are found right on the cell membrane.
Cell Recognition and Sticking Together
- Adhesion proteins help cells recognize each other and stick together. This is very important for building tissues and organs. For example, they play a big role in your immune system, helping your body identify and fight off germs.
Related Topics
Images for kids
-
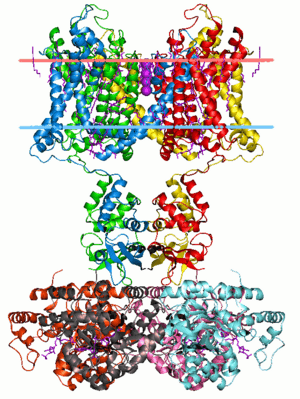
This image shows the detailed structure of a Potassium channel, which is a type of membrane protein. The red and blue lines show the boundaries of the lipid bilayer (the cell's outer layer).
 In Spanish: Proteína de membrana para niños
In Spanish: Proteína de membrana para niños