NGC 501 facts for kids
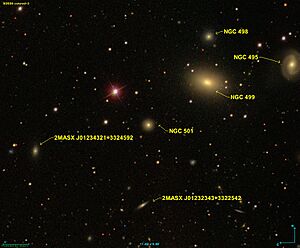
NGC 501 is a type of galaxy called an elliptical galaxy. It is found in the Pisces constellation, which is also known as "The Fish." This galaxy is very far away from our own galaxy, the Milky Way. It is about 230 million light-years from us.
Contents
What is NGC 501?
NGC 501 is a galaxy, which is a huge group of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. The "NGC" in its name stands for "New General Catalogue." This is a famous list of deep-sky objects like galaxies, star clusters, and nebulae. Astronomers use these numbers to identify different objects in space.
This galaxy was first discovered in 1856 by an astronomer named R. J. Mitchell. He used telescopes to find and record many objects in the night sky.
Elliptical Galaxies
NGC 501 is an elliptical galaxy. This means it has a smooth, oval shape, a bit like a stretched-out ball or an egg. Unlike spiral galaxies, which have swirling arms, elliptical galaxies don't have a clear structure. They are often made up of older stars and have less gas and dust for new stars to form.
Elliptical galaxies can be very different in size. Some are tiny, while others are among the largest galaxies in the universe. NGC 501 is a typical example of this kind of galaxy.
Where is Pisces?
The Pisces constellation is where you can find NGC 501. A constellation is a group of stars that form a pattern in the sky, often named after animals, people, or objects. Pisces is one of the 12 constellations of the zodiac, which means it lies along the path the Sun appears to take across the sky.
You can usually see Pisces in the autumn sky in the Northern Hemisphere. It looks like two fish tied together by a string. Finding constellations helps astronomers locate objects like galaxies.
Measuring Distances in Space
When we say NGC 501 is 230 million light-years away, it means the light we see from it today started its journey 230 million years ago. A light-year is a way to measure huge distances in space. It is the distance light travels in one Earth year. Light moves incredibly fast, about 300,000 kilometers (186,000 miles) per second.
Because galaxies are so far away, astronomers use light-years to describe their distances. This helps us understand just how vast the universe is.]
See also
 In Spanish: NGC 501 para niños
In Spanish: NGC 501 para niños
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |