Nitrite facts for kids
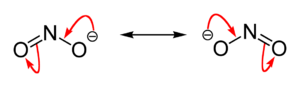
Nitrite is a tiny chemical particle called an ion. Think of it like a building block in chemistry. Its special code name is NO2–. This means it has one nitrogen atom and two oxygen atoms, and it carries a negative electrical charge.
Contents
What are Nitrites?
Nitrites are chemical compounds that contain the nitrite ion. They are usually found as colorless, shiny crystals. A common example you might hear about is Sodium nitrite.
What is an Ion?
An ion is an atom or a group of atoms that has an electric charge. Atoms usually have an equal number of protons (positive charge) and electrons (negative charge), so they are neutral. But if an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion. Nitrite is an ion because it has an extra electron, giving it a negative charge.
How Nitrites Behave
The nitrogen atom inside nitrite has a special "oxidation state" of +3. This number helps chemists understand how atoms share or gain electrons in a chemical bond.
Nitrites are usually strong oxidizing agents. This means they can take electrons from other chemicals, causing those chemicals to change. But they can also be weak reducing agents. This means they can give away electrons to other chemicals. When they give away electrons, they get oxidized themselves and turn into nitrates (NO3–). Nitrates are similar ions but have one more oxygen atom and a different oxidation state for nitrogen.
Where are Nitrites Used?
Nitrites, especially Sodium nitrite, are used in many ways.
- They are often used as curing agents and preservatives in foods like meats. This helps keep the food safe and gives it a specific color and flavor.
- They also play a role in the nitrogen cycle, which is how nitrogen moves through the environment, including the air, soil, and living things.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Nitrito para niños
In Spanish: Nitrito para niños
 | Claudette Colvin |
 | Myrlie Evers-Williams |
 | Alberta Odell Jones |