Nostratic facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Nostratic |
|
|---|---|
| (controversial) | |
| Geographic distribution: |
Europe, Asia except for the southeast, North and Northeast Africa, the Arctic |
| Linguistic classification: | Nostratic |
| Subdivisions: |
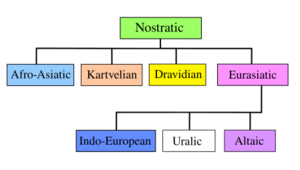
Afroasiatic (usually included)
Dravidian (usually included)
Elamite (sometimes included)
Sumerian (sometimes included)
|
The Nostratic language family is a really interesting idea! It's a hypothetical language family. This means experts think it might have existed a long, long time ago. They believe it was the ancestor of many languages spoken today across Europe and Asia.
The idea is that Nostratic was spoken after the big ice sheets melted. This was before people spread out throughout Europe and Asia.
Contents
What is the Nostratic Hypothesis?
Imagine a giant family tree for languages. The Nostratic idea suggests that many language families we know today all grew from one ancient language. This ancient language is called Proto-Nostratic.
Experts think Proto-Nostratic was spoken between 15,000 and 12,000 BC. That's a super long time ago! This was during the Epipalaeolithic period. It was near the end of the last big ice age.
Languages in the Nostratic Family
Many of today's languages are thought to be descendants of Nostratic. These include:
- Indo-European languages: This huge family includes English, Spanish, Hindi, and many others.
- Uralic languages: Like Finnish and Hungarian.
- Altaic languages: Such as Turkish and Mongolian.
- Kartvelian languages: Spoken mainly in Georgia.
Languages from North Africa and parts of Asia are also often included. These are the Afroasiatic languages and the Dravidian languages. Afroasiatic languages are native to North Africa, the Horn of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, and the Near East. Dravidian languages are spoken in the Indian subcontinent.
Where Does the Name "Nostratic" Come From?
The name "Nostratic" comes from a Latin word. That word is nostrates. It means "us" or "fellow countrymen."
The idea of Nostratic became more popular in the 1960s. This was thanks to linguists in the Soviet Union. They were sometimes called the "Moscovite school." Since the 1990s, this idea has gained more attention in English-speaking countries.
Is the Nostratic Hypothesis Accepted by Everyone?
The Nostratic hypothesis is still a bit controversial. Not all linguists agree on it. Some experts are still unsure if it's true. Others accept it to different degrees. It's an ongoing discussion in the world of language studies.
See also
 In Spanish: Macrofamilia nostrática para niños
In Spanish: Macrofamilia nostrática para niños