Overvoltage facts for kids
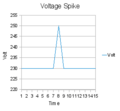
An overvoltage happens when the amount of electricity in a circuit or power line suddenly goes much higher than it's supposed to be. Think of it like a water pipe suddenly getting too much pressure – it can burst! When electricity has too much pressure, it can be very dangerous and cause a lot of damage to electronic devices and even power grids.
Contents
What is an Overvoltage?
An overvoltage means that the electrical voltage (the "pressure" of electricity) in a system rises above its normal, safe level. Every electronic device, from your phone charger to your refrigerator, is designed to work with a specific voltage. If the voltage becomes too high, it can force too much electricity through the device, causing damage.
Why is Overvoltage Dangerous?
Overvoltage can be quite harmful. It can instantly destroy electronic devices, like computers, televisions, and game consoles, by burning out their internal parts. In more serious cases, it can even cause electrical fires in homes or buildings. It can also damage large equipment in power plants or factories, leading to widespread power outages.
What Causes Overvoltage?
Overvoltages can happen for different reasons, some natural and some related to how electricity is produced and delivered.
Natural Causes
- Lightning: One of the most common natural causes is a lightning strike. When lightning hits power lines, a building, or even the ground nearby, it can send a huge surge of electricity through the electrical system. This sudden burst of energy is a very powerful overvoltage.
- Solar Flares: Sometimes, the Sun can release massive bursts of energy called solar flares. These flares send charged particles towards Earth. When these particles interact with Earth's magnetic field, they can create strong electrical currents in power lines, leading to overvoltages across large areas. This is rare but can be very serious.
Man-Made Causes
- Power Grid Issues: Problems within the electrical grid itself can cause overvoltages. For example, if a large power plant suddenly shuts down or if there's a fault in a power line, the electricity in other parts of the grid can briefly surge.
- Switching Surges: When large electrical equipment is turned on or off, it can create temporary voltage spikes. These are usually small, but if they happen repeatedly or are very strong, they can cause damage over time.
- Equipment Failure: Sometimes, a piece of electrical equipment can fail in a way that causes an overvoltage. For instance, if a neutral wire breaks in a three-phase system, it can send too much voltage to some appliances, destroying them.
How Do We Protect Against Overvoltage?
To protect against overvoltage, several methods are used:
- Surge Protectors: These are common devices you can plug your electronics into. They act like a safety valve, diverting excess voltage away from your devices and into the ground.
- Grounding: Proper grounding systems help safely direct unwanted electricity, including overvoltages, into the earth, preventing it from damaging equipment or harming people.
- Power Company Measures: Electricity companies use special equipment like surge arresters and protective relays on power lines and at substations. These devices are designed to detect and safely manage overvoltages before they can cause widespread damage.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sobretensión (electricidad) para niños
In Spanish: Sobretensión (electricidad) para niños