- This page was last modified on 17 October 2025, at 11:18. Suggest an edit.
p53 facts for kids
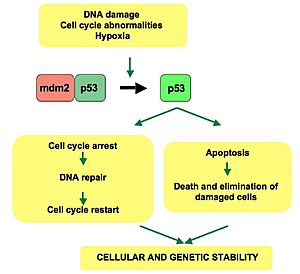
p53 pathway: In a normal cell, p53 is inactivated by its negative regulator, mdm2.
When DNA is damaged, the gene gets activated. Once activated, p53 stops the cell division cycle. Either repair of the cell or apoptosis occurs. How p53 makes this choice is not known
When DNA is damaged, the gene gets activated. Once activated, p53 stops the cell division cycle. Either repair of the cell or apoptosis occurs. How p53 makes this choice is not known
p53 (also known as tp53) is a very important gene found in many living things, including humans. It creates a special protein that helps stop cancer from growing. Because of its vital role, it's often called "the guardian of the genome" – meaning it protects our body's instruction manual.
Contents
What is p53 and How Does It Work?
The p53 protein acts like a superhero inside your cells. Its main job is to keep your DNA healthy and prevent mistakes. Think of DNA as the blueprint for your body. If this blueprint gets damaged, p53 steps in.
When DNA is damaged, the p53 protein gets activated. It then does a few important things:
- It can stop the cell division cycle. This gives the cell time to fix the DNA damage.
- If the damage can't be fixed, p53 can trigger apoptosis. This is a process where the damaged cell safely "self-destructs" to prevent it from causing problems, like becoming cancerous.
This amazing ability to stop damaged cells from growing makes p53 a powerful tumor suppressor gene. It helps keep your body healthy by preventing uncontrolled cell growth.
p53 and Cancer
Sadly, the p53 gene is the most common gene that gets changed or "mutated" in human cancer. More than half of all human cancers have a mutated p53 gene.
When p53 is mutated, it can't do its job properly. It can't stop damaged cells from dividing or make them self-destruct. This allows cells with errors in their DNA to keep growing and multiplying, which can lead to cancer. Scientists are always studying p53 to find new ways to fight cancer.
p53 in Early Development
Interestingly, the p53 protein is found at low levels in human embryonic stem cells. These are very special cells that can turn into any type of cell in the body. Low p53 levels allow these important cells to divide very quickly and create all the different parts of a growing embryo. Once the body is formed, p53 levels increase to protect against DNA damage.
Images for kids
-
A micrograph showing cells with abnormal p53 expression (brown) in a brain tumor. p53 immunostain.
See also
 In Spanish: P53 para niños
In Spanish: P53 para niños