Polyphyly facts for kids
Polyphyly is a term used in cladistics. Cladistics is a way scientists group living things based on their shared ancestors. A polyphyletic group is a collection of organisms whose last common ancestor is not part of that group.
Imagine you group all "flying animals" together. This would include birds, bats, and insects. But their common ancestor did not fly. Each of these groups developed the ability to fly separately. This makes "flying animals" a polyphyletic group.
Contents
What is Polyphyly?
Polyphyly happens when a group includes members from different ancestral lines. These members might share a similar feature. However, they did not get this feature from a single common ancestor. Instead, they developed it on their own.
For example, "warm-blooded animals" is a polyphyletic group. It includes mammals and birds. Mammals and birds are related, but their shared ancestor was not warm-blooded. They each evolved warm-bloodedness separately.
How Scientists Group Life
Scientists use different ways to group living things. The main goal is to show how species are related through evolution.
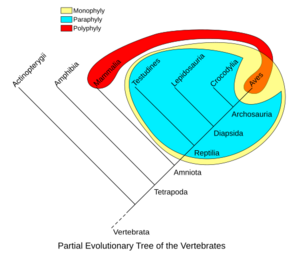
Monophyletic Groups
A monophyletic group includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants. This is like a family tree where you include a grandparent and all their children and grandchildren. Scientists try to make most groups monophyletic.
Paraphyletic Groups
A paraphyletic group includes a common ancestor and some of its descendants. But it leaves out other descendants. For example, "reptiles" are often considered paraphyletic. They include lizards, snakes, and crocodiles. But they usually leave out birds, even though birds evolved from reptiles.
Fixing Polyphyletic Groups
When scientists find a polyphyletic group, they try to "fix" it. They do this to make the classification more accurate. They might remove certain members from the group. Or, they might add the common ancestor to make it a monophyletic group. This helps show the true evolutionary relationships.
Images for kids
-
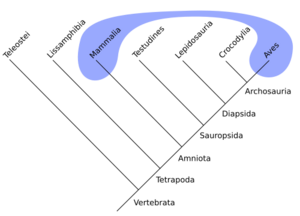
In this phylogenetic tree, the blue and red groups are both monophyletic. They do not share an immediate common ancestor. If they share similar features, they form a polyphyletic group.
See also
 In Spanish: Polifilético para niños
In Spanish: Polifilético para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |