Bitter cherry facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Bitter cherry |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Prunus emarginata leaves and flowers | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Prunus
|
| Species: |
emarginata
|
 |
|
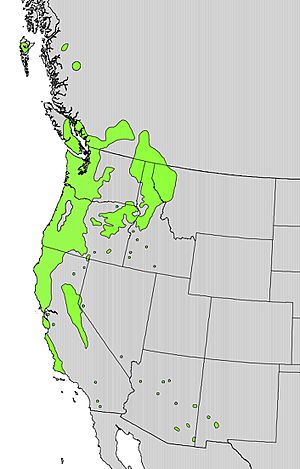
| Natural range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
The Prunus emarginata, also known as the bitter cherry or Oregon cherry, is a type of cherry tree. It grows naturally in western North America. You can find it from British Columbia in Canada all the way south to Baja California in Mexico. It also grows east into parts of Wyoming and New Mexico. This tree often appears in places where the land has been recently changed, like open forests with good soil.
Contents
About the Bitter Cherry Tree
The bitter cherry is a deciduous plant. This means it loses its leaves every autumn. It can be a shrub (a bushy plant) or a small tree. It usually grows between 1 and 15 meters (about 3 to 50 feet) tall. It has a thin, oval-shaped trunk.
Its bark is smooth and can be gray or reddish-brown. You might see small, horizontal lines on the bark called lenticels. These are like tiny pores that help the tree breathe.
The leaves are 2 to 8 centimeters (about 1 to 3 inches) long. They are thin, shaped like an egg, and yellowish-green. Their edges have unevenly sized teeth.
Flowers and Fruit
In spring, the bitter cherry tree produces small flowers. Each flower is about 10 to 15 millimeters (less than an inch) wide. They have five white petals and many thin, hair-like parts called stamens. These flowers smell like almonds. Insects help pollinate them, which means they help the flowers make seeds.
The fruit is a juicy red or purple cherry. Each cherry is about 7 to 14 millimeters (about 0.3 to 0.5 inches) wide. As its name suggests, these cherries taste very bitter. Humans usually do not eat them.
Besides growing from seeds, this plant can also spread in another way. It sends out underground stems. These stems then sprout above the ground, forming a thick patch of new plants.
Different Types of Bitter Cherry
There are two main types, or varieties, of the bitter cherry:
- Prunus emarginata var. emarginata: This type usually grows like a shrub. Its young shoots and leaves are smooth or have very little hair. You can find this type in most places where the bitter cherry grows.
- Prunus emarginata var. mollis (Dougl.) Brew: This type grows into a larger tree. Its young shoots and leaves feel soft and fuzzy. It is mostly found along the coast, from Oregon north to British Columbia.
How Bitter Cherry Grows with Other Plants
Sometimes, the bitter cherry can mix with other cherry trees. For example, it has created a hybrid with the European Prunus avium tree. This happened in the Puget Sound area. The new hybrid plant is called Prunus × pugetensis. It looks like a mix of both parent trees. However, it usually doesn't produce many cherries.
Uses of Bitter Cherry
As mentioned, the bitter cherries are not good for humans to eat because of their taste. But they are an important food source for some animals. Certain birds, especially cedar waxwings, enjoy eating them. Various mammals also eat the cherries. Deer and other farm animals like to eat the leaves of the bitter cherry tree.
Traditional Uses
Some Native Americans, like the Kwakwaka'wakw people, used parts of the bitter cherry plant for traditional medicine. They would use the bark to make poultices (a soft, moist mass applied to the body) or infusions (like a tea). Scientists have also found a natural chemical called prunetin in the bark of this tree.
Bitter Cherry in Nature
The bitter cherry tree is a "host plant" for many different insects. This means that the young forms (larvae) of these insects eat the leaves of the bitter cherry. Some of these insects include:
- The blinded sphinx moth
- The elegant sphinx moth
- Lorquin's admiral butterfly
- The pale tiger swallowtail butterfly
- The small-eyed sphinx moth
- The spring azure butterfly
- The twin-spotted sphinx moth
- The western tiger swallowtail butterfly
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Prunus emarginata para niños
In Spanish: Prunus emarginata para niños






