Pseudophilautus stictomerus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Pseudophilautus stictomerus |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
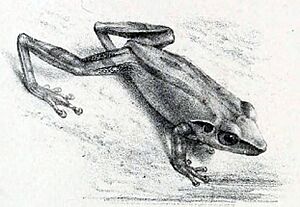
| Pseudophilautus stictomerus from Günther's original description | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Rhacophoridae |
| Genus: | Pseudophilautus |
| Species: |
P. stictomerus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Pseudophilautus stictomerus (Günther, 1876)
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Ixalus stictomerus Günther, "1875" 1876 |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Pseudophilautus stictomerus, also known as the orange-canthal shrub frog, is a type of frog. It belongs to the Rhacophoridae family. This frog lives only in Sri Lanka, meaning it is endemic there. A scientist named Albert Günther first described this species in 1876. He used a single frog found by Colonel Richard Henry Beddome in what was then called 'Ceylon' (now Sri Lanka).
What Does the Orange-Canthal Shrub Frog Look Like?
Male orange-canthal shrub frogs are about 23 millimeters long. Females are a bit bigger, measuring between 25 and 36 millimeters. These measurements are from their snout (nose) to their vent (where waste leaves the body).
They have a long body and a snout that is somewhat pointed. The back of the frog, called the dorsum, is dark brown. A thin yellow stripe runs down the middle of their back. This stripe goes from the tip of their snout all the way to their vent.
One special feature is their bright orange stripes. These stripes are found along the edges of their snout, near their eyes. They also have orange stripes on the edges of their upper eyelids. You can also see orange stripes on the skin folds above their eardrums, which are called supratympanic folds.
Where Do These Frogs Live and What Is Their Habitat?
The orange-canthal shrub frog lives in the low-country wet areas of southwestern Sri Lanka. This means they are found in parts of the country that are not very high up and get a lot of rain.
These frogs are not picky about where they live. They can be found in open areas, like places changed by humans. They also live in forests with thick tree cover. You can find them at different heights, from 60 to 515 meters above sea level.
They often live on shrubs, usually about 1 meter (about 3 feet) above the ground. Sadly, these frogs might be in danger. Things like pollution from farm chemicals and losing their homes are big threats. Their habitats are also changing, which makes it harder for them to survive.
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |


