Virginia rail facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Virginia rail |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| In Morro Bay, California, USA | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Rallus
|
| Species: |
limicola
|
 |
|
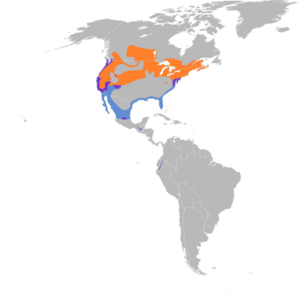
| Breeding Year-round Nonbreeding | |
The Virginia rail (Rallus limicola) is a small bird that lives near water. It belongs to a bird family called Rallidae, which includes other rails. These birds are quite common, even though their homes are sometimes lost. They are shy and hard to spot, so you're more likely to hear them than see them.
Contents
What Does the Virginia Rail Look Like?
Adult Virginia rails are mostly brown. Their backs and heads are a darker shade of brown. They have orange-brown legs. To move through thick plants, their bodies are flat from side to side. This helps them push through dense marsh plants easily.
Their forehead feathers are strong. This protects their heads as they push through plants. Virginia rails have very strong leg muscles. They have long toes that help them walk on plants floating on the water. They have a short tail and a long, thin, reddish beak.
Their cheeks are grey, and they have a light stripe above their eye. Their throat is whitish. Baby Virginia rails, called chicks, are black. Young birds are dark brownish-black on top. Their faces are grayish-brown. Male and female Virginia rails look very much alike. Females are just a little bit smaller.
Adult birds are about 20–27 centimeters (8–11 inches) long. Their wings can spread 32–38 centimeters (13–15 inches) wide. They usually weigh between 65 and 95 grams (2.3–3.4 ounces).
Where Do Virginia Rails Live?
The Virginia rail lives in freshwater and salty marshes. Sometimes they live in salt marshes during the winter. Birds from northern areas fly south for winter. They go to the southern United States and Central America. On the Pacific coast, some Virginia rails stay in the same place all year.
They build their nests in marshes. These areas stretch from Nova Scotia in Canada to Southern British Columbia. They also live in California and North Carolina. You can also find them in Central America. Virginia rails often share their homes with other marsh birds, like the sora.
How Do Virginia Rails Behave?
Virginia rails often run away from danger instead of flying. When they do fly, it's usually for short distances. They also fly when they migrate to warmer places. These birds can also swim and dive underwater. They use their wings to help them move through the water.
What Sounds Do Virginia Rails Make?
This bird makes many different sounds. One common call is a harsh kuk kuk kuk. You can often hear this sound at night. They also make grunting noises. In the spring, they make tick-it or kid-ick calls.
What Do Virginia Rails Eat?
The Virginia rail uses its beak to search for food in mud or shallow water. They also pick up food they see. They mostly eat insects and other small water animals. This includes beetles, flies, dragonflies, crayfish, snails, and earthworms. They can also eat small animals like frogs, fish, and even tiny snakes.
Sometimes, they eat seeds too. Most of their diet is made up of animals. However, they eat more plants in the fall and winter months.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Virginia rails start to find partners around May. The male bird will raise his wings and run back and forth near the female. Both birds will bow to each other. The male will also feed the female. Before they mate, the male approaches the female while making grunting sounds.
Virginia rails are monogamous, meaning they stay with one partner. Both parents help build the nest. They also both take care of the young birds. Only the male bird protects their nesting area. The nest is built like a basket from woven plants. They use plants like cattails, reeds, and grasses.
They also build fake nests around the marsh. This helps to confuse predators. They build their real nest near the bottom of tall plants. These plants create a roof over the nest to hide it.
Female Virginia rails lay 4 to 13 eggs. The eggs are white or light brown with a few gray or brown spots. Each egg is usually about 32 by 24 millimeters (1.25 by 0.94 inches). Both parents take turns sitting on the eggs to keep them warm. This is called incubation. It lasts for 20 to 22 days. During this time, the parents keep adding material to the nest to hide it better.
When the eggs hatch, the parents feed the chicks for two to three weeks. After this, the young birds can take care of themselves. The young can fly in less than a month. The parents' bond breaks after their young become independent.



