Raphe nuclei facts for kids
| Brain: Raphe nuclei | ||
|---|---|---|
Quick facts for kids
|
||
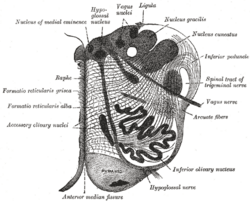
| Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive. (Raphe nuclei not labeled, but 'raphe' labeled at left.) | ||
| Horizontal cross section of the brainstem at the lower pons. The raphe nucleus is labeled #18 in the middle. | ||
| Latin | nuclei raphe | |
The raphe nuclei are a group of small parts, or "nuclei," found in your brain stem. Think of them like tiny control centers. They play a big role in how your brain uses a chemical called serotonin. Serotonin helps control many things, like your mood and sleep.
Contents
Where Are the Raphe Nuclei?
The raphe nuclei are located right in the middle of your brain stem. The brain stem is a vital part of your brain that connects to your spinal cord. These nuclei are found all along the brain stem, from the midbrain down to the medulla oblongata. They are mostly made of special brain cells called neurons that produce serotonin.
What Do Raphe Nuclei Do?
The raphe nuclei are super important for many things your body and mind do. They help with:
- Emotions and Mood: They help control how you feel, your mood, and how you react to stress.
- Body Functions: They help regulate your appetite (how hungry you feel) and your sleep cycles.
- Pain: They play a part in how you sense and deal with pain.
- Movement: They are involved in how your body moves.
How Do They Connect to the Brain?
The raphe nuclei connect with almost every important part of your brain. They send signals to many different areas.
Some of the raphe nuclei, like the nucleus raphe magnus, send signals down to your spinal cord and other parts of the brain stem. Other nuclei, like the nucleus raphe pontis, send signals up to the front parts of your brain. These connections help control your behavior, emotions, memory, and your sleep-wake cycle.
See also
 In Spanish: Núcleos del rafe para niños
In Spanish: Núcleos del rafe para niños
- Locus ceruleus
- Substantia nigra
- Pedunculopontine nucleus
- List of regions in the human brain
 | Bessie Coleman |
 | Spann Watson |
 | Jill E. Brown |
 | Sherman W. White |