Zhangixalus schlegelii facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Zhangixalus schlegelii |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Synonyms | |
|
The Zhangixalus schlegelii is a type of frog often called the Japanese gliding frog or Schlegel's green tree frog. It belongs to the Rhacophoridae family, which includes many tree frogs. This special frog lives only in Japan. You can find it on the main islands like Honshu, Shikoku, Kyushu, and also on the smaller Ryukyu Islands. It was named after Hermann Schlegel, a scientist from the 1800s.
What Does the Japanese Gliding Frog Look Like?
Male Japanese gliding frogs are about 32 to 43 millimeters long. That's about the size of a small paperclip to a large paperclip! Female frogs are a bit bigger, measuring 43 to 53 millimeters.
Male frogs have yellowish-white patches on their thumbs. These are called nuptial pads and help them hold onto the female during mating. Their throats are dark, and they have two small openings for making sounds.
Their fingers and toes have some webbing, but not a lot. The tips of their fingers have flat, round pads. These pads help them grip surfaces. The skin on their back is very smooth. They have a clear fold of skin above their eardrum, but no fold along their sides.
Life Cycle: How Japanese Gliding Frogs Reproduce
Japanese gliding frogs have a very interesting way of laying their eggs. They build special foam nests underground!
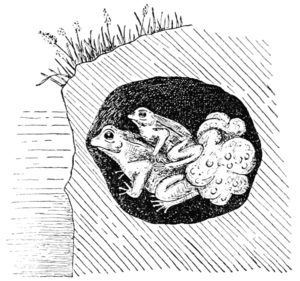
When winter ends, these frogs wake up. They crawl to the edges of rice fields or wet areas. Then, they dig holes in the ground, just above the water level. The female frog, who is bigger, carries the smaller male frog. They both go into the hole, which is about 6 to 9 centimeters wide. The hole is usually 10 to 15 centimeters above the water.
Inside the hole, the female makes the walls smooth. At night, she creates a ball of white, foamy stuff filled with air bubbles. This foam is tough and stretchy, about 6 to 7 centimeters thick. It helps keep the eggs moist and gives them air. The foam comes out with the eggs.
The female then uses her feet to mix the sticky foam. She stretches and closes her toes, mixing air into the foam. This breaks big bubbles into smaller ones. The male also uses his feet to help move the foam. This makes it easier for him to fertilize the eggs.
Once the eggs are fertilized and covered in the protective foam, the parent frogs leave the nest. They go back to living in the trees. The foam nest slowly turns into a liquid. This liquid then flows out through the hole the parents made. It carries the tiny young frogs into the water below.
Where Do Japanese Gliding Frogs Live?
These frogs live in wet areas and forests in hilly and low-lying places. They especially like paddy fields, which are flooded fields used for growing rice. These fields are their main breeding spots.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) keeps track of animals around the world. They do not think the Japanese gliding frog is in danger. It is a common species in Japan.