Rio Salado (Mexico) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Río Salado |
|
|---|---|
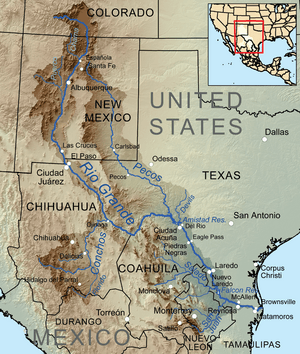
Map of the Rio Grande watershed, showing the Rio Salado joining the Rio Grande south of Laredo.
|
|
| Country | Mexico |
| State | Coahuila, Nuevo León, Tamaulipas |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source | Sierra Madre Oriental |
| River mouth | Rio Grande Falcon International Reservoir 26°52′N 99°19′W / 26.867°N 99.317°W |
| Basin features | |
| Basin size | 60,406 km2 (23,323 sq mi) |
The Río Salado, also known as Río Salado de los Nadadores or Salado River, is an important river in northern Mexico. It is a branch of the larger Rio Grande river, which is called Río Bravo in Mexico. The Río Salado's water flows through parts of the Mexican states of Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas.
River's Journey
The Río Salado starts in the Sierra Madre Oriental mountains in Coahuila. From there, it flows towards the east and northeast. It meets another river, the Sabinas River, inside a large lake created by the Venustiano Carranza Dam.
After leaving this lake, the Salado River continues flowing southeast. It passes through northern Nuevo León and northwestern Tamaulipas. Along its way, it is joined by the Sabinas Hidalgo River. Finally, the Río Salado flows into the Falcon International Reservoir, which is a big lake on the Rio Grande. This meeting point is about 43 kilometers (27 miles) up the Rio Grande from its mouth.
How the River is Used
The Río Salado is very important for the people living nearby.
- Farming: Most of the river's water is used for farming. Farmers use it to water their crops, especially cotton.
- Mining: The river also supports mining activities in the area.
- Fishing: Fishing has become more popular in the river. New types of fish have been put into the water, like gizzard shad, largemouth bass, and white bass. These fish help make fishing a fun activity.
River Health and Environment
The Río Salado faces some challenges with its environment. There are problems with how the natural resources around the river are managed. This means that sometimes, the river's water and the things living in and around it are not cared for as well as they could be. For example, water lilies have been introduced to the river.
See also
 In Spanish: Río Salado de los Nadadores para niños
In Spanish: Río Salado de los Nadadores para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |

