STS-102 facts for kids

ICC (left) and the MPLM Leonardo (center) in Discovery's payload bay
|
|
| Mission type | ISS crew rotation |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA |
| Mission duration | 12 days, 19 hours, 51 minutes, 57 seconds |
| Distance travelled | 8.5 million kilometres (5.3 million miles) |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Space Shuttle Discovery |
| Launch mass | 99,503 kilograms (219,367 lb) |
| Landing mass | 90,043 kilograms (198,511 lb) |
| Payload mass | 5,760 kilograms (12,700 lb) |
| Crew | |
| Crew size | 7 |
| Members |
|
| Launching |
|
| Landing |
|
| EVAs | 2 |
| EVA duration | 15 hours, 17 minutes |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 8 March 2001, 11:42 UTC |
| Launch site | Kennedy LC-39B |
| End of mission | |
| Landing date | 21 March 2001, 07:33:06 UTC |
| Landing site | Kennedy SLF Runway 15 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Perigee | 370 kilometres (230 mi) |
| Apogee | 381 kilometres (237 mi) |
| Inclination | 51.5 degrees |
| Period | 92.1 minutes |
| Docking with ISS | |
| Docking port | PMA-2 (Destiny forward) |
| Docking date | 10 March 2001, 06:38 UTC |
| Undocking date | 19 March 2001, 04:32 UTC |
| Time docked | 8 days, 21 hours, 54 minutes |
  The STS-102 crew portrait. |
|
STS-102 was an important Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The mission used the Space Shuttle Discovery and launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, in March 2001. Its main goals were to deliver supplies to the ISS and to swap out the crews of Expedition 1 and Expedition 2. During this mission, astronauts performed a spacewalk that lasted 8 hours and 56 minutes, which was the longest spacewalk ever at that time!
Contents
Meet the Astronauts of STS-102
This section lists the brave astronauts who flew on the STS-102 mission. Some astronauts went up to the ISS, and others came back down to Earth.
| Position | Launching Astronaut | Landing Astronaut |
|---|---|---|
| Commander | Fifth spaceflight |
|
| Pilot | First spaceflight |
|
| Mission Specialist 1 | Third spaceflight |
|
| Mission Specialist 2 | First spaceflight |
|
| Mission Specialist 3 | Expedition 2 Fourth and last spaceflight ISS Commander/ISS Soyuz Commander |
Expedition 1 Fourth and last spaceflight ISS Commander |
| Mission Specialist 4 | Expedition 2 Fifth and last spaceflight ISS Flight Engineer |
Expedition 1 Second spaceflight ISS Soyuz Commander |
| Mission Specialist 5 | Expedition 2 Fifth and last spaceflight ISS Flight Engineer 2 |
Expedition 1 Fifth spaceflight ISS Flight Engineer |
Spacewalks on STS-102
Astronauts on STS-102 performed two spacewalks, also known as Extravehicular Activities (EVAs). During a spacewalk, astronauts leave the spacecraft to work in the vacuum of space.
- Spacewalk 1: Voss and Helms
- Start Time: March 11, 2001 – 05:12 UTC
- End Time: March 11, 2001 – 14:08 UTC
- Duration: 8 hours, 56 minutes (This was a record-breaking spacewalk!)
- Spacewalk 2: Thomas and Richards
- Start Time: March 13, 2001 – 05:23 UTC
- End Time: March 13, 2001 – 11:44 UTC
- Duration: 6 hours, 21 minutes
What Did STS-102 Do?
This mission was called Space Station Assembly Flight ISS-5A.1. It was very important for building the International Space Station.
Bringing Supplies to the ISS
STS-102 was the first time the Multi Purpose Logistics Module (called Leonardo) was used. This module carried many supplies to the space station. It had up to 16 special racks, called International Standard Payload Racks, which were installed in the US Lab module of the ISS.
Moving Equipment Outside the Station
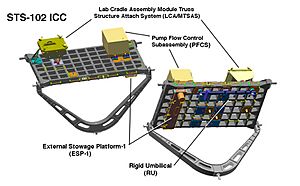
The mission also carried an Integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC). This carrier had the External Stowage Platform-1 (ESP-1) attached to its bottom. ESP-1 was later moved and placed on the side of the 'Destiny' module. It acts as a storage place for spare parts and equipment needed for the ISS. The two spacewalks helped move these items to the outside of the Destiny module.
Wake-up Music in Space
NASA has a cool tradition of playing music to wake up astronauts in space. This started during the Gemini program and was first used for the Apollo 15 mission. The songs are often chosen by the astronauts' families. They usually have a special meaning to an astronaut or relate to what they will be doing that day.
See also
 In Spanish: STS-102 para niños
In Spanish: STS-102 para niños
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |