Sailboat facts for kids
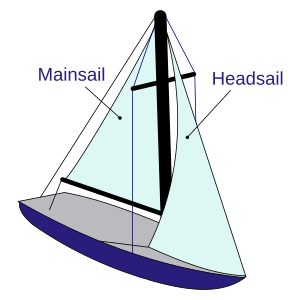
A sailboat is a boat that uses sails to move across the water. The wind pushes against the sails, making the boat go. Sailboats come in many sizes. They range from small sailboards to very large sailing ships. Most sailboats have two main sails: a mainsail and a head sail (also called a jib). Sometimes, when the wind is coming from behind, an extra sail called a spinnaker is used.
Contents
Types of Sailboats
Sailboats have changed a lot over time. Today, we can tell different types apart by their size, how their body (hull) is shaped, the kind of keel they have, what they are used for, and how many masts and sails they carry.
Here are some popular types of sailboats with one main body (called a monohull):
Cutter Sailboats
A cutter is a lot like a sloop. It has one mast and one mainsail. But the mast on a cutter is placed further back. This allows the boat to have two front sails: a jib and a staysail. Cutters used to be common in races. Now, they are often used for longer trips. The extra front sail helps them handle strong winds better.
Catboat Sailboats
A catboat has a single mast placed very far forward on the boat. It usually does not have a jib. Most modern catboats only have one sail, which is the mainsail. Older, traditional catboats could carry more sails from a special type of rig called a gaff rig.
Dinghy Sailboats
A dinghy is a small, open sailboat. People often use them for fun, learning to sail, or as a small boat to get to and from a bigger boat. They are popular for young sailors. This is because they are short, easy to use, and simple to take care of. Dinghies usually have three or fewer sails: the mainsail, jib, and spinnaker.
Ketch Sailboats
Ketches are similar to sloops. However, they have a second, shorter mast. This second mast is behind the main mast but in front of the rudder. This smaller mast is called the mizzen mast, and its sail is called the mizzen sail.
Schooner Sailboats
A schooner has a mainmast that is taller than its front mast (called the foremast). This is how you can tell it apart from a ketch or a yawl. A schooner can even have more than two masts. The front mast is always shorter than the main mast. Traditional schooners often had extra sails above their main sails. Many modern schooners use a Bermuda rig, which has triangular sails.
Sloop Sailboats
The sloop is the most common type of modern sailboat. It has one mast and two sails. These are usually a Bermuda rigged mainsail and a headsail. This simple design is very good for sailing against the wind.
Some sloops have a "fractional rig." This means the front sail (forestay) is attached below the very top of the mast. This design allows the mainsail to be adjusted for better performance. It also makes the smaller headsail easier for a small crew to handle.
Yawl Sailboats
A yawl is much like a ketch. It also has a shorter mizzen mast. But on a yawl, this mizzen mast is placed behind the rudder. Its main purpose is to help balance the boat, not to provide a lot of power.
Boat Bodies (Hulls)
Most traditional sailboats have one body, called a monohull. But boats with multiple bodies, like multi-hull catamarans (two bodies) and trimarans (three bodies), are becoming more popular.
Monohull boats usually use heavy weights (ballast) to stay stable. This can make them less easy to turn and slower to speed up. Also, if a monohull fills with water, it might sink unless it has special foam or air tanks.
Multihull boats stay stable because of their wide shape and multiple bodies. Some multihulls are built to be very light. They can have foam-filled areas that help them float. Some modern trimarans are even designed so they cannot sink. This means they will stay afloat even if all their compartments fill with water.
The Keel
Every boat has a keel. It is like the backbone of the boat's body (hull). In older boats, the keel was the main structure everything else was built upon.
Most modern monohull boats have "fin keels." These are heavy and deep but short compared to the boat's length. Older boats often had "full keels," which ran along half or more of the boat's length.
A newer type is the "winged keel." It is short and not very deep. But it has two "wings" that stick out sideways, holding a lot of weight. Even newer are "canting keels." These keels can move the weight at the bottom of the boat to the side that is facing the wind. This helps the boat carry more sails and go faster.
Multihull boats do not need heavy keels. They get their stability from their wide design and multiple bodies.
The Mast
The mast is the tall pole that holds the sails. On small sailboats, the mast can be put in place by hand. The bottom of the mast might sit in a holder above the boat's keel or on the deck. Some masts can be raised using a hinge.
Some masts are only supported at the bottom (keel) and at the deck. These are called "unstayed" masts. Most masts rely on strong wires (called standing rigging) to hold them up from the sides and front-to-back. Masts taller than about 7.6 meters (25 feet) usually need a crane to be put in place. They are typically placed through the cabin down to the keel.
Images for kids
-
A sailboat on Lake Constance, Germany.
-
A Bermuda rigged sloop in Convict Bay, Bermuda, around 1879.
See also
 In Spanish: Embarcación de vela para niños
In Spanish: Embarcación de vela para niños