Salinity facts for kids
Salinity is a scientific term that tells us how much salt is dissolved in water. When scientists talk about salinity, they are usually talking about the amount of sodium chloride (the same kind of salt you use for cooking) found in water.
Scientists measure salinity by looking at how many grams of salt are in 1,000 grams of water. If there is 1 gram of salt in 1,000 grams of water, they say it's 1 part per thousand. This is written as 1‰.
Contents
Different Types of Water Salinity
Not all water has the same amount of salt. Here are the different types:
Fresh Water
- Fresh water has very little salt, less than 0.1% (or 1‰).
- You usually find fresh water in rivers and lakes. This is the water we drink!
Brackish Water
- Brackish water has a bit more salt than fresh water, usually between 0.1% and 3% (1‰ to 30‰).
- This type of water is often found where a river meets the sea, in places called estuaries. It's a mix of fresh and salty water.
Saline Water
- Saline water is what we usually call "salty water." It contains between 3% and 5% salt (30‰ to 50‰).
- The water in the oceans is typically saline, with about 3.5% salt (35‰).
Brine Water
- Water that has more than 5% salt (over 50‰) is called brine.
- Some lakes and bodies of water are so salty they are considered brine. For example, the Dead Sea is extremely salty, with about 15% salt (150‰) at its surface.

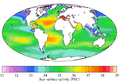
Average salinity of the surface for the World Ocean per year. This map shows how salty the ocean surface is in different places.
Images for kids
-
Annual mean sea surface salinity for the World Ocean. This map shows the average saltiness of the ocean surface each year.
See also
 In Spanish: Salinidad para niños
In Spanish: Salinidad para niños

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
Salinity Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.