Sapir-Whorf hypothesis facts for kids
The Sapir–Whorf hypothesis is a big idea in linguistics, which is the study of language. It suggests that the language we speak actually shapes how we think and see the world around us. It's like saying your language isn't just a way to talk about reality, but it also helps create your reality!
Contents
What is the Sapir–Whorf Hypothesis?
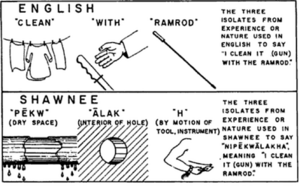
This idea explores the connection between language and thought. It asks: Does the way your language is built influence how you understand time, space, or even colors? For example, if your language has many words for snow, do you see snow differently than someone whose language has only one word?
Strong vs. Weak Ideas
The Sapir–Whorf hypothesis actually has two main parts, often called the "strong" and "weak" versions:
- Strong version: This idea says that language completely determines how we think. It means you can't even think about something if your language doesn't have words or grammar for it. Most scientists today don't fully agree with this strong version.
- Weak version: This idea is more widely accepted. It suggests that language influences or affects our thought, but it doesn't completely control it. It means our language can make it easier or harder to think about certain things, or it can guide our attention to specific details.
Who Were Sapir and Whorf?
The hypothesis is named after two important American linguists: Edward Sapir and Benjamin Lee Whorf. They both studied different languages and noticed interesting connections between language and culture.
Edward Sapir
Edward Sapir (1884–1939) was a very influential linguist and anthropologist. He was interested in how language connects to culture and personality. He studied many Native American languages and saw how their structures were very different from European languages. Sapir believed that language was not just a tool for communication but also a guide to social reality.
Benjamin Lee Whorf
Benjamin Lee Whorf (1897–1941) was a student of Sapir. He was actually a chemical engineer by profession, but he became very passionate about linguistics. Whorf is famous for his studies of the Hopi language, spoken by the Hopi people in Arizona. He claimed that the Hopi language had a very different way of talking about time compared to English, which he believed led to a different understanding of time for Hopi speakers.
Examples of Language and Thought
Let's look at some simple examples to understand how language might influence our thinking:
- Colors: Some languages have many different words for shades of blue, while others might only have one word for both blue and green. Does this mean speakers of those languages see colors differently?
- Directions: In English, we use "left," "right," "front," and "back." Some languages, like Guugu Yimithirr in Australia, use only cardinal directions like "north," "south," "east," and "west." So, instead of saying "move the cup to your right," they might say "move the cup to the west." This means speakers of such languages are always aware of their exact orientation.
How Language Shapes Our World
The Sapir–Whorf hypothesis suggests that our language can highlight certain things and make others less noticeable. It can influence:
- How we categorize things: Different languages group objects or ideas in unique ways.
- Our memory: What we remember might be influenced by how our language helps us describe events.
- Our attention: Language can make us pay more attention to specific details in our environment.
Why is This Idea Important?
Understanding the Sapir–Whorf hypothesis helps us appreciate the amazing diversity of human languages and cultures. It shows us that there isn't just one "right" way to see the world. It encourages us to be more open-minded about how different people think and communicate, which is super important in our connected world. It also makes us think about how our own language shapes our thoughts every day!
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Hipótesis de Sapir-Whorf para niños
In Spanish: Hipótesis de Sapir-Whorf para niños
 | Shirley Ann Jackson |
 | Garett Morgan |
 | J. Ernest Wilkins Jr. |
 | Elijah McCoy |