Saturated and unsaturated compounds facts for kids
In chemistry, compounds can be described as either saturated or unsaturated. This tells us how many atoms they can hold. Think of it like a sponge: a saturated sponge is full of water, and an unsaturated one can still soak up more.
A saturated compound is a type of chemical compound that is "full." This means its atoms are connected by only single bonds. There is no room for any more atoms to join the molecule. Because they are already full, saturated compounds do not easily react with other atoms by adding them.
An unsaturated compound is the opposite. It is "not full." These compounds have at least one double bond or triple bond between their atoms. These extra bonds mean there is still room for more atoms to connect. Unsaturated compounds are more reactive because they can easily break these double or triple bonds to add more atoms.
Contents
What are Saturated Compounds?
Saturated compounds are very stable. They are made of atoms that are joined together by single bonds. This means each atom has all the connections it can possibly make. For example, a carbon atom can form four bonds. In a saturated compound, it will have four single bonds to other atoms.
Alkanes: Common Saturated Compounds
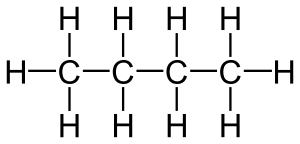
A great example of saturated compounds are the alkanes. Alkanes are a family of simple organic compounds. They contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms. All the bonds in alkanes are single bonds.
- Methane (CH4) is the simplest alkane. It has one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms.
- Ethane (C2H6) has two carbon atoms linked by a single bond, and each carbon is also bonded to three hydrogen atoms.
- Propane (C3H8) and butane (C4H10) are other common alkanes. You might know propane from gas grills and butane from lighters.
Because alkanes only have single bonds, they are considered saturated. They do not easily add more atoms to their structure.
What are Unsaturated Compounds?
Unsaturated compounds are different because they have "extra" bonds. These can be double bonds or triple bonds between carbon atoms. These extra bonds make them more reactive. They can easily break these bonds to add more atoms, like hydrogen, to become saturated.
Alkenes and Alkynes: Examples of Unsaturated Compounds
Two main types of unsaturated compounds are alkenes and alkynes.
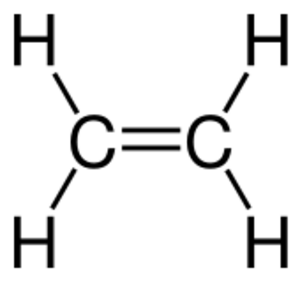
- Alkenes have at least one carbon-carbon double bond.
* Ethene (C2H4), also known as ethylene, is the simplest alkene. It has two carbon atoms connected by a double bond. Each carbon is also bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Ethene is used to ripen fruits.
- Alkynes have at least one carbon-carbon triple bond.
* Ethyne (C2H2), also known as acetylene, is the simplest alkyne. It has two carbon atoms connected by a triple bond. Each carbon is also bonded to one hydrogen atom. Ethyne is used in welding torches.
These double and triple bonds are like "empty seats" where more atoms can join. This is why unsaturated compounds can undergo "addition reactions." In these reactions, atoms are added across the double or triple bond, turning the unsaturated compound into a saturated one.
Why is This Important?
Understanding saturated and unsaturated compounds is important in many areas of chemistry and daily life.
- Fats and Oils: In food, fats can be saturated or unsaturated. Saturated fats (like butter) usually come from animals and are solid at room temperature. Unsaturated fats (like olive oil) usually come from plants and are liquid. Unsaturated fats are often considered healthier.
- Plastics: Many plastics are made from unsaturated compounds that link together in long chains. This process is called polymerization.
- Fuels: Many fuels, like gasoline, are mixtures of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Knowing whether a compound is saturated or unsaturated helps chemists predict how it will behave and what it can be used for.
See also
 In Spanish: Compuestos saturados e insaturados para niños
In Spanish: Compuestos saturados e insaturados para niños