Secure Shell facts for kids
| Protocol stack | |
| Purpose | secure connection, remote access |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Tatu Ylönen, Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) |
| Introduction | 1995 |
| OSI layer | Transport layer through application layer |
| Port(s) | 22 |
| RFC(s) | RFC 4250, RFC 4251, RFC 4252, RFC 4253, RFC 4254 |
The Secure Shell Protocol (often called SSH) is a special way to connect to computers over a network safely. It uses secret codes, called encryption, to protect your information. This means you can use it to log into a computer far away or send commands to it, and no one else can easily see what you are doing.
SSH was created for computers that work like Unix systems. It was made to replace older, less secure ways of connecting, like Telnet or Remote Shell. These older methods sent your password and other information as plain text, which was like sending a postcard with your secrets written on it. Anyone who could see the network could read them! SSH fixes this by encrypting everything, making it like sending your secrets in a locked box.
A computer scientist from Finland, Tatu Ylönen, invented SSH in 1995. He made it after someone tried to steal passwords on his university network. He wanted a safer way to connect. Over time, SSH became very popular. Today, the most common version is called OpenSSH. It was released in 1999 and is free to use. You can find SSH on almost all types of computers, including macOS, Linux, and even newer versions of Windows.
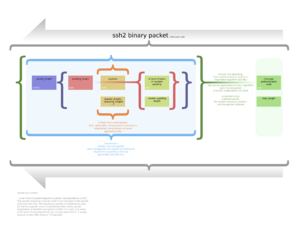
SSH works like a conversation between two computers: a client and a server. The client is your computer, and the server is the computer you want to connect to. SSH has three main parts that work together:
- The transport layer sets up the secure connection and makes sure the server is who it says it is.
- The user authentication protocol checks that you are allowed to connect to the server.
- The connection protocol lets you do many things at once over that one secure connection.
Contents
How SSH Works
SSH uses a special kind of secret code called public-key cryptography. This helps the remote computer prove it's real. It also lets the computer check that you are allowed to connect.
One simple way SSH works is by using two special keys: a public key and a private key. Think of it like a lock and two keys. The public key is like a lock you can give to anyone. The private key is the only key that can open that lock, and you keep it secret.
When you want to connect to a server, you put your public key on that server. When you try to connect, your computer uses your private key to prove it's you. The private key never leaves your computer. SSH just checks that you have the correct private key that matches the public key on the server. This way, you often don't even need to type a password!
It's very important to make sure the public key you get from a server is the correct one. If you accept a fake public key from a hacker, they could pretend to be the real server and trick you.
Managing SSH Keys
On many computer systems, like Linux, your public keys are stored in a special file called `~/.ssh/authorized_keys`. This file is kept very safe so only you can change it. If your public key is on the server and you have the matching private key on your computer, you usually don't need a password to log in. For extra safety, you can even put a password on your private key.
There are tools, like `ssh-keygen`, that help you create these public and private key pairs.
What SSH Is Used For
SSH is mostly used to log into a remote computer's command line, which is like a text-based way to control a computer. You can type commands and make the remote computer do things.
But SSH can do much more!
- Secure File Transfer: You can use SSH to send files safely between computers using tools like SFTP or SCP.
- Tunneling: SSH can create a secure "tunnel" for other types of network traffic. This is like building a secret, encrypted pathway through the internet. For example, you can use it to access websites or services that are usually blocked.
- Remote Applications: You can even run graphical programs from a remote computer and see them on your screen, all through the secure SSH connection.
SSH uses a client-server setup. Your computer runs an SSH client program. The remote computer runs an SSH daemon (a background program) that waits for connections. Most modern operating systems, like macOS, Linux, and even recent versions of Windows, come with SSH built-in.
SSH is also very important for cloud computing. It helps you connect safely to virtual computers in the cloud, protecting them from being directly exposed to the internet.
The standard "door" or port that SSH uses on the internet is port 22. This port is well-known for SSH connections.
How SSH Was Developed
Version 1
In 1995, Tatu Ylönen, a researcher in Finland, created the first version of SSH, called SSH-1. He did this after a password-stealing attack happened on his university's network. He wanted to replace older, insecure ways of connecting, like Telnet and FTP, which didn't protect information. He chose port 22 for SSH because it was between the ports used by FTP (21) and Telnet (23).
Ylönen released his SSH program for free in July 1995, and it quickly became popular. By the end of 1995, about 20,000 people in 50 countries were using it.
In December 1995, Ylönen started a company called SSH Communications Security to sell and improve SSH. The first versions used some free software, but later versions became more like private, paid software. By the year 2000, it was estimated that 2 million people were using SSH.
Version 2
In 2006, a new and improved version of the SSH protocol, called SSH-2, became a standard. This version is much safer and has new features, but it doesn't work with SSH-1. For example, SSH-2 uses stronger ways to exchange secret keys and check if data has been changed. It also uses better encryption methods, like AES, which are much harder to break than older ones.
A cool feature of SSH-2 is that you can have many different "sessions" or conversations happening at the same time over just one SSH connection. Because SSH-2 is so much better and more popular, many newer SSH programs only support SSH-2.
OpenSSH: The Free Version
In 1999, some developers wanted a free version of SSH that anyone could use and change. They started working on a project called OSSH, based on an older, free version of SSH. Soon after, the developers of OpenBSD (a type of operating system) took that code and created OpenSSH.
By 2005, OpenSSH was the most popular SSH program. It's still actively updated and supports the secure SSH-2 protocol. OpenSSH is now the default SSH program on many operating systems.
The Future of SSH: SSH3
In 2023, some researchers suggested a new idea called SSH3. This new version would work differently, using newer internet technologies like HTTP/3 and QUIC. It aims to make connections even faster and more secure. SSH3 would also use modern security features like TLS 1.3 and X.509 certificates.
However, the name "SSH3" is still being discussed. Some people think it's so different from the original SSH that it should have a completely new name.
Common Uses of SSH
SSH is a very flexible tool that can be used on many different computer systems, including Linux, macOS, and Microsoft Windows. Here are some common ways people use SSH:
- Logging In: To securely log into a remote computer's command line. This replaces older, unsafe methods like Telnet.
- Running Commands: To run a single command on a remote computer without fully logging in.
- Automatic Login: To set up connections that don't need a password, using SSH keys. This is great for automated tasks.
- File Syncing: To copy and back up files safely and efficiently, often with a tool called rsync.
- Port Forwarding: To create a secure tunnel for specific network traffic, like making a local port on your computer connect to a port on a remote server.
- Secure VPN: To create a full encrypted VPN (Virtual Private Network) for all your internet traffic, though this is mostly supported by OpenSSH.
- X Window Forwarding: To run graphical applications from a remote computer and display them on your local screen.
- Secure Browsing: To browse the web through a secure, encrypted connection using SSH as a proxy.
- Mounting Remote Folders: To make a folder on a remote server appear like a local folder on your computer using SSHFS.
- Remote Management: To manage and monitor servers from a distance.
- Mobile Development: To work on programs for mobile or embedded devices that support SSH.
- Secure File Transfers: SSH is the base for several secure file transfer methods:
* SCP: A simple way to copy files over SSH. * rsync: More efficient than SCP for syncing files. * SFTP: A secure replacement for the older FTP protocol. * FISH: Another protocol for transferring files using SSH commands.
How SSH Is Built
The SSH protocol is built in layers, like a cake with different layers doing different jobs:
- The transport layer is the bottom layer. It usually uses TCP (a common internet protocol) and listens on port 22. This layer sets up the initial secure connection, checks the server's identity, and handles encryption. It also makes sure that keys are re-exchanged regularly for continued security.
- The user authentication layer is the middle layer. It handles how you prove who you are to the server. The server doesn't ask you for a password directly; your SSH client asks you, and then sends the proof to the server. Common ways to prove your identity include:
* Password: Just typing your password. * Public Key: Using your public and private key pair, which is very secure. * Keyboard-interactive: Where the server might ask you a series of questions to log in.
- The connection layer is the top layer. It lets you have many different "channels" or conversations happening at the same time over one SSH connection. For example, you could be running a command in one channel and transferring a file in another, all securely.
This layered design makes SSH very flexible. It can be used for many things beyond just a secure command line.
Security and Vulnerabilities
SSH is designed to be very secure, but like all software, it can have weaknesses.
SSH-1 Vulnerabilities
The first version of SSH (SSH-1) had some design flaws. For example, in 1998, a problem was found that allowed someone to sneak extra information into an encrypted SSH stream. Later, other problems were found that could allow attackers to take control of a server. Because of these issues, SSH-1 is now considered old and unsafe. Most modern SSH programs only use SSH-2.
Other Attacks
In 2008, a theoretical weakness was found that could allow a small part of encrypted data to be guessed. This was fixed by using a different encryption method.
More recently, in 2023, a new type of attack called the Terrapin attack was discovered. This attack could affect most current SSH programs. However, it's difficult to carry out and mostly just causes connections to fail. SSH developers quickly released updates to fix this problem. To be fully safe, both your SSH client and the server you connect to need to be updated.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Secure Shell para niños
In Spanish: Secure Shell para niños
- Brute-force attack
- OpenSSH
- Secure Shell tunneling
- Web-based SSH