Siphon (mollusc) facts for kids
A siphon is a cool, tube-like part found in some water animals called molluscs. These include snails, bivalves (like clams and oysters), and cephalopods (like squids and octopuses). This special tube helps them move water or air in and out of their bodies.
Siphons are used for many important things. They help molluscs breathe, move around, find food, and even with reproduction.
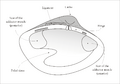
The siphon is actually part of the mollusc's mantle, which is a soft layer of tissue. The water flows through the siphon into or out of the mantle cavity. This is a space inside the mollusc's body.
Some snails have just one siphon. Clams and other bivalves usually have two siphons. Squids and octopuses have a single siphon, which is also called a hyponome.
Contents
How Siphons Help Molluscs
Siphons are super important for molluscs to survive in the water. They act like a special pathway for water to enter and leave the animal's body.
Breathing Underwater
Many molluscs use their siphons to breathe. They pull water into their bodies through one siphon. This water then flows over their gills, which take out the oxygen. After getting the oxygen, the water leaves through another siphon. It's like how we breathe air, but they breathe water!
Moving Around
Siphons can also help some molluscs move. Squids and octopuses, for example, use their hyponome for "jet propulsion." They quickly push water out of their siphon, which makes them shoot backward through the water. It's a very fast way to escape danger!
Finding Food
Some molluscs use their siphons to find food. Clams might pull in water with tiny food particles. Snails can use their siphon to "sniff" out food in the water, like a nose. This helps them find yummy things to eat.
Staying Safe
Siphons can also help molluscs stay safe. If a clam senses danger, it can quickly pull its siphons back inside its shell. This helps protect the soft parts of its body from predators.
Different Kinds of Siphons
Molluscs have different types of siphons depending on their lifestyle.
Siphons in Snails
Many snails, especially those that live in the ocean, have one siphon. This siphon is often used to bring water over their gills for breathing. Some snails, like the ones that eat other animals, use their siphon to sense chemicals in the water, helping them find their prey.
Siphons in Clams and Oysters
Bivalves like clams, mussels, and oysters often have two siphons. One is called the inhalant siphon, which sucks in water. The other is the exhalant siphon, which pushes water out. This constant flow of water helps them breathe and filter food from the water. Some siphons, like those of the geoduck, can be very long!
Siphons in Squids and Octopuses
Cephalopods have a single siphon, called a hyponome. This siphon is very strong and muscular. It's mainly used for jet propulsion, allowing these clever animals to move quickly through the water. They can also use it to squirt ink to confuse predators.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sifón (anatomía) para niños
In Spanish: Sifón (anatomía) para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |