Somatosensory system facts for kids

The somatosensory system is like your body's amazing "feeling" network. It's a sensory system that helps you sense many different things. This system lets you feel touch and pressure, temperature (like if something is warm or cold), and even pain. It also helps you feel things like itch and tickle.
Beyond just touch, this system helps you know where your body parts are. This is called proprioception. It lets you feel your muscles moving and how your joints are positioned. This includes knowing your posture and how your body is moving. It also covers "visceral senses," which are feelings from inside your body, like a stomach ache.
You might think touch is just one of your five main senses. But when you touch something, you actually feel many different things at once. You might feel pressure (like its shape, how soft it is, its texture, or if it's vibrating). You also feel its temperature and sometimes pain. So, "touch" is really a mix of several different senses working together. In medicine, scientists often use the term somatic senses to describe all these different ways your body feels things.
Contents
What is the Somatosensory System?
The somatosensory system is a complex network. It includes special cells, nerves, and parts of your brain. These all work together to collect information from your body and send it to your brain. Your brain then figures out what those feelings mean. This system is always active, helping you understand your surroundings.
How Do We Feel Things?
When you touch something, tiny sensors in your skin, muscles, and joints get activated. These sensors are called receptors. They turn the physical feeling (like pressure or heat) into electrical signals. These signals then travel along nerves to your spinal cord. From there, they go up to your brain.
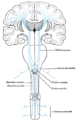
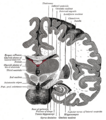
Your brain has special areas that receive these signals. One important area is the somatosensory cortex. This part of your brain helps you understand where the feeling is coming from and what it is. For example, it tells you if you're touching something rough or smooth, or if it's hot or cold.
Different Kinds of Touch
The somatosensory system helps us feel many different types of sensations. These can be grouped into a few main categories:
- Touch and Pressure: This is about feeling contact with objects. It includes light touches, deep pressure, and even vibrations. It helps you tell the shape and texture of things.
- Temperature: This lets you feel if something is warm, hot, cool, or cold. Special receptors in your skin are sensitive to different temperatures.
- Pain: Pain is an important signal that tells your body something might be wrong. It can be sharp, dull, burning, or aching. Pain receptors protect you from harm.
- Proprioception: This is your body's sense of its own position and movement. It helps you know where your arms and legs are without looking. It's how you can touch your nose with your eyes closed.
Why is This System Important?
The somatosensory system is super important for everyday life. It helps you:
- Explore the world: By touching things, you learn about them.
- Stay safe: Feeling pain or extreme temperatures warns you of danger.
- Move around: Proprioception helps you balance and coordinate your movements.
- Connect with others: Touch is a big part of how we interact with people, like holding hands or getting a hug.
Other pages
Images for kids
-
The cortical homunculus, a map of somatosensory areas of the brain, was devised by Wilder Penfield.
See also
 In Spanish: Sistema somatosensorial para niños
In Spanish: Sistema somatosensorial para niños