Stagflation facts for kids
Stagflation is a special word used in economics. It describes a time when a country's economy faces three tough problems all at once. These problems are:
- When there is almost no growth in how much a country produces (this is called stagnation).
- When prices for goods and services are going up very fast (this is called inflation).
- When many people cannot find jobs (this is called unemployment).
Normally, economists thought these three things couldn't happen at the same time. They believed that if prices were rising, more things would be made, and more people would have jobs. But stagflation shows that this isn't always true. It's a very difficult problem for a country to fix.
Contents
What Does Stagflation Mean?
The word "stagflation" is a mix of two words: "stagnation" and "inflation."
- Stagnation means things are not growing or moving forward. In economics, it means the country is not making more goods or services.
- Inflation means that prices for everyday things like food, clothes, and toys are going up. This means your money buys less than it used to.
So, stagflation means the economy is stuck (stagnant) and prices are rising quickly (inflation). At the same time, many people are out of work.
Where Did the Word Come From?
A British politician named Iain Macleod first used the word "stagflation." He said it in a speech to the British Parliament in 1965. Later, he became a very important financial leader in the government.
Why Is Stagflation a Problem?
Stagflation is a big challenge for leaders trying to manage a country's economy. This is because the usual ways to fix inflation can make unemployment worse. And the ways to fix unemployment can make inflation worse. It's like trying to push down on one side of a seesaw, only to make the other side go up. Once stagflation starts, it can be very hard and costly to stop.
The Misery Index
To understand how bad stagflation is, economists sometimes use something called the Misery Index. This index is a simple number. You get it by adding the inflation rate to the unemployment rate. A higher Misery Index means people are having a tougher time because of high prices and job losses.
How Does Stagflation Start?
Stagflation often begins when the cost of making things goes up. For example, if the price of oil suddenly increases, it costs more to transport goods. This makes everything more expensive. When it costs more to make an item, companies have to raise their prices.
When prices go up, people might buy less. Also, companies might not want to invest money in making more things if they think people won't buy them. If companies make fewer things, they need fewer workers. This leads to more people losing their jobs. So, you have:
- Higher costs for making things.
- Higher prices for what people buy.
- Fewer things being made.
- More people without jobs.
All these factors together create stagflation.
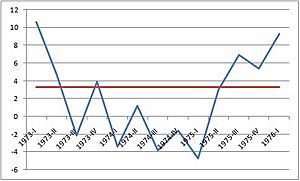
The 1970s Recession
A famous example of stagflation happened in the 1970s. From 1973 to 1975, many countries in the Western world faced a tough economic time. This period is known as the 1973–75 recession. Before this, there had been a long time of good economic growth after World War II.
But in the 1970s, things changed. Countries saw both high unemployment and high inflation at the same time. This was a big surprise to many economists and was a clear example of stagflation.
See also
 In Spanish: Estanflación para niños
In Spanish: Estanflación para niños