Striated antbird facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Striated antbird |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Thamnophilidae |
| Genus: | Drymophila |
| Species: |
D. devillei
|
| Binomial name | |
| Drymophila devillei (Ménégaux & Hellmayr, 1906)
|
|
| Subspecies | |
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The striated antbird (Drymophila devillei) is a small bird found in the Amazon Rainforest in South America. It belongs to a bird family called Thamnophilidae, which are often known as antbirds. These birds are special because they often follow swarms of army ants to catch insects that try to escape the ants.
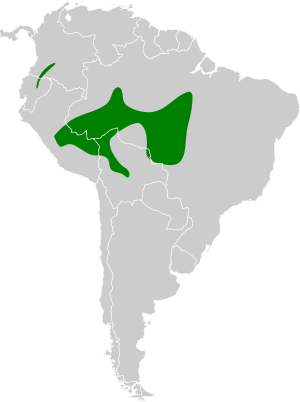
This bird lives in the western and south-central parts of the Amazon. There are two main types, or subspecies, of the striated antbird. One type lives in the west, and the other, called D. d. subochracea, lives in the south-central Amazon. Sometimes, D. d. subochracea is also called the Xingu antbird.
Contents
Where the Striated Antbird Lives
The striated antbird has a large area where it lives. This area covers parts of southeastern Peru, northwestern Bolivia, and Brazil. It mainly lives in the southwest and south-central parts of the Amazon Basin.
Antbird's Range in Bolivia
In Bolivia, the bird's home range splits into two parts. Birds in the northwest are found near the rivers that flow into the Madeira River in Brazil. The eastern Bolivian birds live near the Guaporé River, which forms part of the border between Bolivia and Brazil. This river flows into the Madeira River. The western Bolivian range also stretches southeast into central Bolivia.
Separate Groups of Antbirds
There is also a separate group of striated antbirds that lives far away from the main group. This smaller group is found in a narrow strip, about 100 kilometers (60 miles) wide and 400 kilometers (250 miles) long, in northern Ecuador and the very southwest of Colombia. This is called a disjunct population, meaning it's separated from the main population.
Rivers in the Antbird's Habitat
The striated antbird's range includes areas near several important rivers that flow into the Amazon River. These include the Madeira River, the Purús River, and the Juruá River to the west. The eastern edge of their habitat is near the Tapajós River and its headwaters, which border the northwest part of the Cerrado region.
See also
 In Spanish: Tiluchí estriado occidental para niños
In Spanish: Tiluchí estriado occidental para niños
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |


