Subcutaneous tissue facts for kids
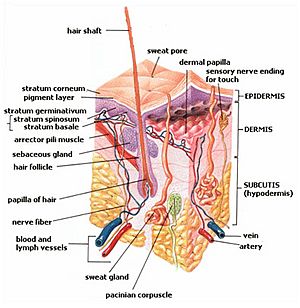
The subcutaneous tissue, also known as the hypodermis, is the deepest layer of your skin. It sits right below the dermis, which is the middle layer, and the epidermis, which is the top layer you can see. Think of it as the padding and connection layer between your skin and the muscles and bones underneath.
In humans, this important layer is where your body stores most of its fat cells. It also contains white blood cells that help fight infections, and many blood vessels that bring nutrients and oxygen.
The hypodermis also helps connect your skin to the muscles below it. It does this using strong bands of connective tissue, sometimes called deep fascia. This connection allows your skin to move smoothly over your muscles.
What Does the Hypodermis Do?
The hypodermis has several important jobs:
- Energy Storage: It stores fat, which your body can use for energy when needed.
- Insulation: The fat acts like a natural blanket, helping to keep your body warm.
- Protection: It provides a cushion that protects your bones and organs from bumps and impacts.
- Connecting Skin: It firmly attaches your skin to the muscles and other tissues underneath.
Images for kids
-
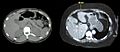
Cross-sections of the torso of a person of normal weight (left) and an obese person (right), taken by CT scan. Note the 3.6 cm (1.4 inches) of subcutaneous fat on the obese person.
See also
 In Spanish: Tejido subcutáneo para niños
In Spanish: Tejido subcutáneo para niños