Tectonics facts for kids
- Further information: Plate tectonics
Tectonics is the study of how Earth's outer layer, called the crust, is built and shaped. It looks at big features like mountains and valleys. It also studies how the crust can bend (this is called folding) or break (this is called faulting or cracking).
The word "tectonics" comes from a Latin word that means "building." It's a part of geology, which is the science that studies Earth's solid parts, like rocks and soil. Tectonics helps us understand the huge forces and movements that create the landforms we see on our planet.
What is Tectonics?
Tectonics focuses on the lithosphere. This is Earth's rigid outer shell, which includes the crust and the very top part of the mantle. Think of it like the hard skin of an apple. Tectonics explores how this shell moves and changes over millions of years.
How Earth's Surface Changes
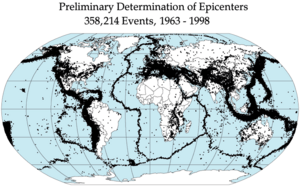
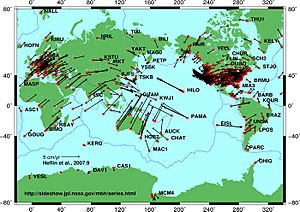
Tectonics helps us understand how big land features are made. For example, it explains mountain building, which is how huge mountain ranges form. It also helps us understand why earthquakes and volcanoes happen in certain areas around the world. These events are all connected to the movement of Earth's plates.
You can learn even more about these movements by looking into plate tectonics. This is a big idea in geology that explains how Earth's outer shell is broken into several large pieces, or "plates," that are always slowly moving.
Why Tectonics Matters
Studying tectonics is important for many reasons:
- It helps us understand erosion patterns. Erosion is when wind, water, or ice wear away rocks and soil. Tectonics affects where and how erosion happens.
- It guides geologists who are looking for valuable resources. For example, understanding tectonic movements can help find places where petroleum (oil) or metal ores (like iron or copper) might be hidden deep underground.
Images for kids
-
The famous San Andreas Fault in California, where two tectonic plates slide past each other.