Telefónica facts for kids

Logo since 2021
|
|

Headquarters in Madrid, Spain
|
|
|
Formerly
|
Compañía Telefónica Nacional de España (1924–1984) |
|---|---|
| Public | |
| Traded as | BMAD: TEF NYSE: TEF (ADR) BVL: TEF (ADR) |
| ISIN | [https://isin.toolforge.org/?language=en&isin=ES0178430E18 ES0178430E18] |
| Industry | Telecommunications |
| Founded | 19 April 1924 |
| Headquarters |
Telefónica Building, Madrid, Spain
Registered office Distrito Telefónica, Madrid, Spain Corporate headquarters |
|
Area served
|
Europe, Mainland China, United States, Latin America |
|
Key people
|
Marc Murtra (chairman and CEO) |
| Products |
|
| Revenue | |
|
Operating income
|
|
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
|
Number of employees
|
104,150 (2021) |
| Subsidiaries |
|
Telefónica, S.A. is a big Spanish company that provides telecommunications services. It has its main offices in Madrid, Spain. Telefónica is one of the largest phone and mobile network providers in the world. It offers services like landline phones, mobile phones, internet, and TV subscriptions. The company operates in many countries across Europe and the Americas.
Besides the Telefónica name, the company also uses other well-known brands. These include Movistar, O2, and Vivo.
Contents
How Telefónica Started
Telefónica began in Madrid in 1924. Its original name was Compañía Telefónica Nacional de España (CTNE). At first, a company called ITT was a major owner. In 1945, the Spanish government bought a large part of the company.
Until 1997, Telefónica was the only phone company in Spain. Even after other companies joined the market, Telefónica remained very strong. Today, Telefónica works in over 20 countries in Europe and America.
In 2023, a company from Saudi Arabia, STC Group, became Telefónica's biggest shareholder. This means they owned the largest part of the company. Later in 2023, the Spanish government also decided to buy a share of Telefónica.
Who Owns Telefónica?
Telefónica is owned by many different shareholders, over 1.5 million people and companies. Its shares are traded on stock markets in Spain, London, New York, Lima, and Buenos Aires. Because Telefónica is important for national defense, the Spanish government has a say in who buys large parts of the company.
The main owners include:
- The Government of Spain (through SEPI): 10%
- CaixaBank: 5.07%
- STC Group: 4.9%
- Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria (BBVA): 4.9%
Where Telefónica Operates
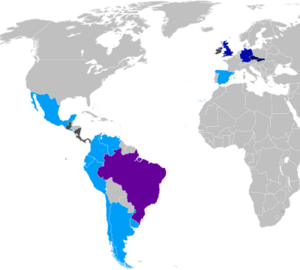
Telefónica in Europe
Spain
Telefónica is a very large company in Spain. It uses the Movistar and O2 brands there. Movistar is the biggest provider of internet and phone services in Spain. Telefónica's fiber optic internet network in Spain is the largest in Europe. The company is also working to switch off its older copper phone lines.
Germany
Telefónica used to own Telefónica Deutschland. In 2006, Telefónica bought O2, a mobile phone company from the UK. O2 also offered services in Germany. After this, Telefónica Deutschland and O2 Germany joined together to form Telefónica Germany.
In 2014, Telefónica Germany bought another company called E-Plus. This made their network the largest in Germany by customer numbers.
United Kingdom
In 2005, Telefónica bought O2, a mobile phone company in the UK. O2 kept its name and its offices in the UK.
In 2020, Liberty Global (which owns Virgin Media) and Telefónica (which owns O2) decided to combine their businesses in the UK. This deal was worth a lot of money. On June 1, 2021, Virgin Media and O2 UK Ltd officially merged. The new company is called Virgin Media O2. Telefónica owns half of this new company.
France
Since 2011, Telefónica has worked with a French company called Bouygues Telecom. They offer telecommunication services to large international companies. In 2015, they created a new company together to expand these services.
Telefónica in the Americas
Telefónica uses the Movistar brand for mobile phones across Latin America. In Brazil, it uses the Vivo brand. Telefónica is the largest mobile operator in Chile, Venezuela, Brazil, and Peru. The company has plans to sell most of its Latin American businesses. This will allow them to focus more on their main markets in the UK, Spain, Germany, and Brazil.
Argentina
Telefónica owns Telefónica de Argentina. This is the biggest landline phone company in Argentina. It provides internet and phone services in the southern part of the country and around Buenos Aires. The mobile phone services are offered through Movistar.
Brazil
Telefónica has a very large landline phone business in Brazil. It provides internet and phone services in the state of São Paulo, which is a very important economic area. Telefónica also owns most of the mobile phone company Vivo in Brazil. Telefónica has been in Brazil since 1996.
In 2009, the Brazilian telecom agency (ANATEL) told Telefónica to stop selling its internet service for a while. This was because of problems with the service. Telefónica had to improve its network before it could sell internet again.
Chile
Telefónica owns Telefónica Chile, which used to be called CTC. It is the biggest landline phone and internet provider in Chile. Telefónica has been in Chile since 1989. In 2009, Telefónica Chile changed its name to Movistar for all its services, including mobile, landline, and TV.
Colombia
In 2006, Telefónica bought a large part of Colombia Telecomunicaciones (TELECOM), a government-owned company. This made Telefónica the biggest landline operator in Colombia. Mobile services are offered through the Movistar brand. The company is now known as Telefónica - Telecom.
Costa Rica
Telefónica started offering services in Costa Rica in 2011. It uses its Movistar brand there.
Ecuador
Telefónica Móviles Ecuador started in 2004 after Telefónica bought another company called OTECEL S.A. It operates as Movistar and is one of the main mobile operators in Ecuador.
Panama
Telefónica began operating in Panama in 2004. It uses the Movistar name for its mobile services.
Peru
Telefónica has been in Peru since 1994. It owns the largest landline phone company in the country. The company offers phone and internet services across Peru. Mobile services are provided through Movistar. Since 2011, Telefónica has used the Movistar brand for all its services in Peru.
Puerto Rico
Telefónica has a presence in Puerto Rico through several of its business units. It used to have mobile services there under the Movistar brand, but it sold that network in 2007.
Venezuela
In 2004, Telefónica took over Telcel Bellsouth in Venezuela, which was the largest mobile operator at the time. After changing its name to Movistar, it updated its network to offer faster mobile internet.
United States
Telefónica USA, based in Miami, Florida, helps international companies that have offices in Latin America and Europe. Telefónica USA also runs a data center in Miami.
Telefónica in Asia
China
In 2009, Telefónica and China Unicom, a Chinese company, agreed to own parts of each other's companies. In 2011, they increased this partnership. Telefónica now owns a part of China Unicom, and China Unicom owns a part of Telefónica.
In 2018, they started a new partnership to work together on the "internet of things." This helps their customers use smart devices and services in China, Europe, and Latin America with one special SIM card.
Past Operations
Czech Republic
In 2005, Telefónica bought Český Telecom, the main phone company in the Czech Republic. This deal also included Eurotel, a mobile phone company. In 2006, both companies merged and were renamed Telefónica O2 Czech Republic. Later, Telefónica sold its part of the company in 2013. The company was allowed to keep using the O2 brand name.
Slovakia
In 2006, Telefónica became the third mobile phone operator in Slovakia, using the O2 brand. It started offering services in 2007. This company was also sold along with the Czech Republic business.
Ireland
Telefónica bought O2 in Ireland as part of its purchase of O2 UK in 2005. Telefónica Ireland became the second largest mobile phone company in Ireland. In 2013, Telefónica agreed to sell its O2 Ireland business to Hutchison Whampoa. O2 Ireland then merged with Three Ireland in 2015.
Italy
Telefónica used to own a part of Telco, a company that controlled a share of Telecom Italia. Telecom Italia is Italy's former government-owned phone company. Telefónica planned to buy more of Telco, but there were concerns about competition in Brazil. In 2014, Telefónica decided to sell its shares in Telecom Italia.
Central and South America
Telefónica started operations in Guatemala in 1998. In 2004, it bought BellSouth Guatemala and relaunched mobile services as Movistar.
In 2019, América Móvil announced it would buy Telefónica's operations in Guatemala and El Salvador. The sale in Guatemala was approved. However, the sale in El Salvador did not go through.
Also in 2019, Millicom announced it would buy Telefónica's operations in Panama, Costa Rica, and Nicaragua. This deal was completed in August 2019. Telefónica made these sales to focus on its larger markets and reduce its debt.
Sponsorships
Cycling
Since 2011, Telefónica has sponsored a Spanish cycling team called Movistar Team.
Football
Telefónica sponsors several national football teams. These include the Spain team (through Movistar+) and teams like Brazil (through Vivo), Mexico, Colombia, Peru, and Venezuela in the Americas.
Rugby
O2 is the main sponsor of the England national rugby team.
Motor Sports
Telefónica, through Movistar, sponsored the Yamaha Motor Racing team in MotoGP from 2014 to 2018. They also sponsored other motorcycle racing teams in the past.
In Formula One, Telefónica sponsored the Minardi F1 Team in 1999 and 2000. They also sponsored the Renault F1 Team from 2004 to 2006. Telefónica was also a title sponsor for the Spanish Grand Prix from 2006 to 2010.
In the World Rally Championship, Telefónica sponsored the SEAT Sport WRC Team and the Ford WRC Team.
Sailing
Movistar and Telefónica have sponsored teams in the round-the-world Volvo Ocean Race in 2005–06, 2008–09, and 2011–12.
eSports
Telefónica sponsors an eSports team called "Movistar Riders" through its Movistar brand.
Innovation and Partnerships
Telefónica is involved in new technologies. It supports the HbbTV initiative, which helps combine regular TV with internet applications.
Telefónica's Wayra program, started in 2011, invests in and helps new startup companies. It has supported over 300 companies.
In 2014, the Firefox web browser added a feature called Firefox Hello for video chats. This feature was powered by Telefónica.
In 2017, Nokia and Telefónica agreed to work together to develop 5G technology.
In January 2025, Telefónica hired JPMorgan to look into possibly selling its business in Argentina.
Leaders of Telefónica
| Year | Chairperson |
|---|---|
| 1924-1945 | Estanislao de Urquijo y Ussía |
| 1945-1964 | José Navarro-Reverter Gomis |
| 1964-1973 | Antonio Barrera de Irimo |
| 1973-1976 | José Antonio González-Bueno |
| 1976-1980 | Tomás Allende y García-Baxter |
| 1980-1982 | Salvador Sánchez-Terán |
| 1982-1989 | Luis Solana |
| 1989-1996 | Cándido Velázquez-Gaztelu |
| 1996-2000 | Juan Villalonga |
| 2000-2016 | César Alierta |
| 2016-2025 | José María Álvarez-Pallete |
| 2025-act. | Marc Murtra |
Being a Dominant Company
Telefónica has received fines in the past for being too dominant in the market. This means they were so big that it made it hard for other companies to compete fairly. For example, in 2007, the European Commission fined Telefónica for its actions in the Spanish internet market. They said it hurt Spanish customers and businesses.
Some customer groups in Spain have also reported problems with canceling Telefónica's internet service. They claim that it takes too long to cancel and that bills sometimes continue even after cancellation.
Network Rules
In 2010, the CEO of Telefónica, Cesar Alierta, said that his company wanted to charge big internet companies like Google for using their network. He felt that these companies were benefiting without helping to pay for the network's costs. He also said that Telefónica would try to offer more of its own content.
See also
 In Spanish: Telefónica para niños
In Spanish: Telefónica para niños
- Movistar
- List of telecommunications companies
- List of telecommunications regulatory bodies
- List of mobile network operators