Three Kingdoms of Korea facts for kids
| The Three Kingdoms of Korea | |
|---|---|
|
|
|
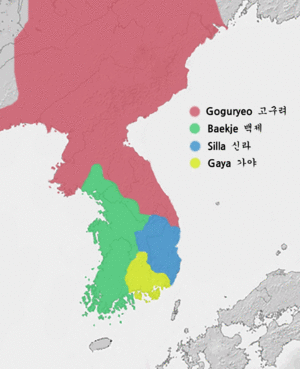
| A Map of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, at the end of 5th century |
|
| Korean Name | |
| Better romanization | Samguk |
| Hangul | 삼국 |
| Hanja | 三國 |
The Three Kingdoms of Korea were three powerful kingdoms: Goguryeo, Baekje, and Silla. These kingdoms existed for a long time, from about 57 BC to 668 CE. During this period, there were also smaller kingdoms and groups like Gaya, Dongye, Okjeo, and Buyeo.
Baekje played an important role in sharing knowledge. It helped spread Chinese writing, Chinese culture, a type of Buddhism called Han Buddhism, and new technologies to Japan.
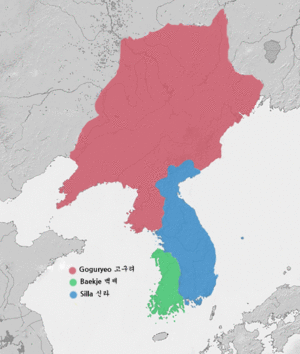
The Three Kingdoms period ended in 668 CE. Silla formed an alliance with the Tang Dynasty of China. Together, they conquered Baekje first, and then Goguryeo. This led to Korea being united under a new kingdom called Later Silla. However, the Tang Dynasty took control of the northern parts of Korea for a while. After this, Korea was divided again during the North and South States period.
Besides old Chinese records, we learn about this time from two important Korean books: Samguk Sagi and Samguk Yusa. The word "Samguk" (Hangul: 삼국, Hanja: 三國) simply means "Three Kingdoms" in Korean.
Contents
Exploring the Three Kingdoms: Key Facts
This section will help you understand more about each of the main kingdoms.
Goguryeo: The Northern Powerhouse
Goguryeo was the largest of the three kingdoms. It was located in the northern part of the Korean Peninsula and parts of Manchuria. This kingdom was known for its strong military and often fought against Chinese dynasties. Goguryeo's people were brave and skilled warriors.
Baekje: The Cultural Bridge
Baekje was located in the southwestern part of the Korean Peninsula. It had strong ties with China and Japan. Baekje was very important for spreading culture and technology. They shared Chinese writing, Buddhist ideas, and advanced skills with Japan. This helped Japan develop its own culture.
Silla: The Unifier
Silla started in the southeastern part of the Korean Peninsula. It was initially the smallest and least developed of the three. However, Silla grew stronger over time. It eventually formed an alliance with China's Tang Dynasty. This alliance allowed Silla to conquer Baekje and Goguryeo. Silla then united most of the Korean Peninsula under one rule. This period is known as Later Silla.
Life During the Three Kingdoms Period
What was daily life like for people living in these ancient kingdoms?
Society and People
Society in the Three Kingdoms was often divided into different groups. There were kings, nobles, common people, and sometimes slaves. The nobles had a lot of power and land. Most people were farmers, working hard to grow food.
Culture and Art
The Three Kingdoms period was a time of great cultural growth. Buddhism became very popular and influenced art, architecture, and daily life. Many beautiful temples, statues, and paintings were created. People also enjoyed music, dance, and poetry. Each kingdom developed its own unique style of art.
Technology and Innovation
People in the Three Kingdoms were very clever. They developed new technologies for farming, building, and warfare. For example, they built impressive fortresses and tombs. They also made beautiful pottery and metalwork, including famous gilt-bronze statues.
The End of the Three Kingdoms
The unification of Korea under Silla was a major event.
The Silla-Tang Alliance
Silla's alliance with the Tang Dynasty was a turning point. The Tang Dynasty wanted to expand its influence. Silla needed help to defeat its rivals, Baekje and Goguryeo. This partnership led to the fall of the other two kingdoms.
Unification and Its Impact
After conquering Baekje in 660 CE and Goguryeo in 668 CE, Silla became the dominant power. This unification brought an end to centuries of conflict between the three kingdoms. It created a more stable and unified Korean state. However, the Tang Dynasty's presence in the north led to further conflicts before Korea was fully independent.
Images for kids
-
Roof tiles found at Goguryeo archaeological sites in the Han River valley, displayed at the National Museum of Korea.
See also
 In Spanish: Tres Reinos de Corea para niños
In Spanish: Tres Reinos de Corea para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |