Transcription (genetics) facts for kids
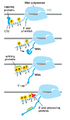
Transcription is a super important process in all living things. It's how your cells make a copy of a specific part of your DNA into a new molecule called RNA. Think of DNA as a huge cookbook with all the recipes for life. Transcription is like copying one recipe from that cookbook onto a smaller note card (RNA) so it can be used to make something specific, like a protein.
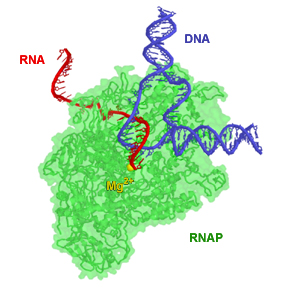
A special helper molecule called RNA polymerase does this copying. It reads the DNA recipe and builds a matching RNA strand. This first RNA strand is often called 'pre-messenger RNA'.
After this first copy is made, some parts of it, called introns, are removed. These introns are like extra, non-coding bits in the recipe. Another helper, called a spliceosome, cuts them out. The remaining important parts, called exons, are then joined together. This final, edited copy is called messenger RNA (mRNA). It's called messenger RNA because it carries the genetic message from the DNA to the cell's protein-making factories. Transcription is the very first step in using the instructions stored in your genes.
What is a Transcription Unit?
The specific section of DNA that gets copied into an RNA molecule is known as a transcription unit. This unit contains different types of instructions:
- Instructions that control when and how much protein is made.
- Sections that don't code for proteins (the introns).
- Sections that do code for the building blocks of proteins, called amino acids (these are the exons).
How DNA is Copied
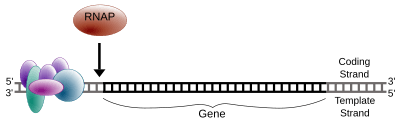
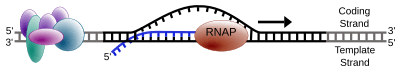
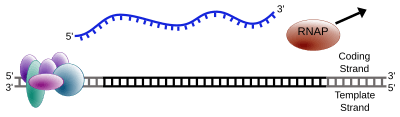
Just like when DNA makes copies of itself (DNA replication), only one of the two DNA strands is used for transcription. This strand is called the template strand. It acts as the guide for building the new RNA molecule. The other DNA strand is called the coding strand. Its sequence is almost the same as the new RNA molecule, except that DNA has thymine (T) while RNA has uracil (U).
The RNA polymerase reads the DNA template strand in a specific direction (from 3' to 5'). It then builds the new RNA strand in the opposite direction (from 5' to 3'). The RNA polymerase starts by attaching to the beginning of a gene on the DNA template strand. This starting point is called a promoter.
In 2006, a scientist named Roger D. Kornberg won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his important discoveries about how transcription works in complex organisms like humans.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
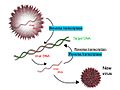
Scheme of reverse transcription, which is like transcription but in reverse.
See also
 In Spanish: Transcripción genética para niños
In Spanish: Transcripción genética para niños
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |