Italian crested newt facts for kids
The Italian crested newt (Triturus carnifex) is a type of newt that belongs to the Salamandridae family. These amazing amphibians are known for their unique crests, especially the males during breeding season. They spend part of their lives in water and part on land.
Quick facts for kids Italian crested newt |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Juvenile with yellow dorsal stripe | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Triturus
|
| Species: |
carnifex
|
 |
|
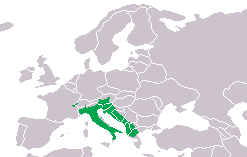
| Range of T. carnifex in Europe | |
Contents
Where Italian Crested Newts Live
The Italian crested newt lives in parts of the Balkans and Italy. They love to breed in water and can stay there for up to four months.
Choosing the Right Pond
These newts prefer deep water because they are good swimmers. They can move freely and are not pushed around by water currents. They also like ponds without lots of fish. This is because fish might eat their young.
Newts in northern Europe prefer colder ponds. Adult newts usually arrive at these ponds between February and May. They then leave between July and October. In warmer ponds, they arrive and leave more quickly. Scientists think that newts move into ponds more after it rains. This is because rain makes the air more humid, which helps them travel.
How Altitude Affects Newts
Newts living in higher, colder places tend to be bigger. Scientists found that both male and female newts grow larger in colder temperatures. Larger females can carry more eggs. This gives them an advantage for having more babies.
Being larger also helps these newts control their body temperature. Since they are cold-blooded, a bigger body helps them stay warmer when it's cold. More food and water in an area can also lead to bigger newts.
Human Impact on Newt Homes
Sadly, human activities have changed the newt's habitat a lot. As cities and factories grow, the newt's natural homes get broken up. This can make it harder for newts to find mates. It can also lead to them becoming less healthy over time.
When fish are put into isolated ponds, it's bad news for newts. The fish often eat the newt larvae (babies), which causes the newt population to drop.
How Italian Crested Newts Breathe
Adult Italian crested newts breathe in a few ways. They mostly breathe through their skin. They also use their lungs and the inside of their mouths. They use their lungs more when there isn't much oxygen in the water. They also use them when they are very active, like when they are looking for a mate or hunting for food.
Amazing Blood Cells
Scientists have found something very interesting about these newts. If they don't have enough red blood cells, they can still breathe for a while. After about two weeks, their bodies start making new cells. These new cells help to replace the missing red blood cells.
Body Changes for Seasons
During winter, a special signal in their body tells them to go into the water. This signal also helps them take in more water from their surroundings. In the summer, when they live more on land, their bodies change again. This helps them keep the right balance of salts and water.
Newt Behavior and Life
To avoid fighting with other newts, the Italian crested newt often reproduces in the deeper parts of a pond. They are also more active at night. Because they are larger, they can sometimes eat smaller newt species.
Female newts that are ready to lay eggs are very good at controlling their body temperature. They also prefer warmer temperatures than other females and males.
Newts and Pollution
Unfortunately, Italian crested newts are sensitive to pollution.
Cadmium and Newts
Cadmium is a metal that gets into the environment from factories and waste. Even small amounts of cadmium can harm newts. It can mess with their "stress glands," which are important for their health.
Other Harmful Chemicals
Another chemical called nonylphenol can also hurt newts. This chemical often leaks from sewers. When newts are exposed to it, it can lower their "stress hormones." These hormones are made by their stress glands and help them deal with difficult situations.
Images for kids