Trollius laxus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Trollius laxus |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Ranunculales |
| Family: | Ranunculaceae |
| Genus: | Trollius |
| Species: |
T. laxus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Trollius laxus Salisb. 1807
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The American Globeflower, Trollius laxus is a rare and protected flowering plant. It grows naturally in the northeastern United States. This plant can only survive in wetlands and marshes. Because of this, groups of these plants are always at risk from changes in water levels where they live.
Contents
Where It Lives
Trollius laxus is a rare plant that grows back every year. It is found only in a small area of fens. Fens are a type of wetland fed by water from underground. These areas are rich in calcium. In these fens, many T. laxus plants can grow close together.
You can also find them in Oregon, Washington, British Columbia, and the Rocky Mountains of Colorado. In the spring, T. laxus is one of the first flowers to bloom in the Rocky Mountains. Its growth is limited by how much sunlight it gets and how much water is in the ground.
Wetlands and marshes usually have a lot of groundwater. This means water levels are often high. High water can lead to a lack of oxygen and fewer nutrients in the soil. Scientists think the plants learned to live in these conditions. This way, they have less competition for sunlight from other plants.
T. laxus likes wet places, but it can also grow in drier spots if there is enough sunlight. More sunlight helps these plants grow bigger. However, there's a limit to how much light is good. Too much sun, especially with dry spells, can make it hard for T. laxus to compete with other plants. To get the right amount of light and water, T. laxus has to live in a small area. This is why it is not found everywhere.
Home and How It Lives
The American Globeflower is a plant that lives for many years. It mostly grows in wet, forested areas. These places have cold, underground water that is a bit salty. This plant is one of the first to bloom in the spring. In Connecticut, it flowers from mid-April to early May. Its seeds are ready by mid-June. The wind and water then help spread the seeds.
Trollius laxus has only a few good pollinators. These include the sweat bee, the Cuckoo bee, and a type of fly called a Tachinidae fly. Slugs and snails can eat the leaves. This can harm the plant and affect other plants around it. When slugs eat T. laxus seedlings, it makes it harder for them to survive. Other plants and animals nearby can also cause problems. If nearby plants are removed, T. laxus is less likely to be eaten. It also grows better and makes more seeds.
T. laxus can also be found in wet forests. This means it might be good at growing under the shade of trees. People who study these plants have seen that both light and water levels affect how strong the T. laxus plants are. They also affect how many plants are in a group. Other plants competing for space can also limit where T. laxus can grow.
What It Looks Like
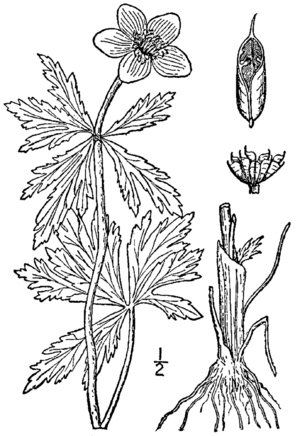
Botanists can easily spot Trollius laxus because of its bright yellow, round flowers. When there are no flowers, other features help identify the plant. It is a plant with soft stems that grow one to two feet tall. It has thick, strong roots and leaves that grow from the base.
The plant can have one or more stems. Each stem has one cream or pale yellow flower. The flower can be up to 5 centimeters (about 2 inches) wide. It has 5 to 7 petal-like Sepals. The real petals are very small. They look like tiny leaves with sweet nectar glands at their base.
Each leaf of Trollius laxus has five leaflets. These leaflets are divided into three parts and spread out flat from the end of the leaf stem. Each leaflet has sharp, toothed edges. The leaves grow on stalks that come from the bottom of the plant.
Flowers and Fruits
This plant is one of the first to bloom in the spring. The flower stalk is usually longer than the leaf stalk. The flowers grow at the very tip of the flower stalk. Each stalk has only one flower. Each flower has five sepals with visible veins. In the middle of the flower are many stamens. There are also ten to fifteen petals that are deep yellow or orange. Hidden among the petals are five or more separate fruits.
The fruits of Trollius laxus are dry. Each fruit pod usually has three to six seeds. Many of these pods grow together on the stems. The flowers of T. laxus can be white to yellow. They have nectar glands at their base and can grow up to five centimeters wide. Both the number of flowers and fruits are higher when there is more sunlight. This might be because pollinators can fly farther after visiting a warmer flower than a colder one.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Trollius laxus para niños
In Spanish: Trollius laxus para niños