United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit facts for kids
Quick facts for kids United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit |
|
|---|---|
| (9th Cir.) | |
 |
|
 |
|
| Location | James R. Browning U.S. Court of Appeals Building
More locations
|
| Appeals from |
|
| Established | March 3, 1891 |
| Judges | 29 |
| Circuit Justice | Elena Kagan |
| Chief Judge | Sidney R. Thomas |
The United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit (often called the 9th Cir.) is the largest of the 13 special appeals courts in the United States's federal court system. It hears cases from federal trial courts in nine western states and two Pacific Island areas. This court helps make sure laws are applied fairly across a huge part of the country.
Contents
What the 9th Circuit Does
The 9th Circuit is a U.S. federal court. It has the job of reviewing decisions made by lower courts. This is called appellate jurisdiction. It checks if the rules were followed correctly in trials.
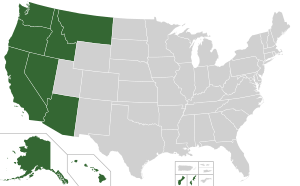
States and Territories Covered
The 9th Circuit hears appeals from federal district courts in many places. These include:
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Central California
- Eastern California
- Northern California
- Southern California
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Montana
- Nevada
- Oregon
- Eastern Washington
- Western Washington
It also reviews cases from courts in two U.S. territories:
- Guam
- Northern Mariana Islands
Where the Court Meets
The main office of the Ninth Circuit is in San Francisco, California. It is the largest appeals court with 29 active judges. The court also holds meetings in Seattle, Portland, and Pasadena.
Sometimes, judges travel to other places in the circuit to hear cases. This helps lawyers save time and money on travel. Cases from the northern areas are usually heard in Seattle or Portland. Cases from southern California are heard in Pasadena. Cases from northern California, Nevada, Arizona, and Hawaii are heard in San Francisco.
History of the 9th Circuit
The 9th Circuit has grown a lot since it started in 1891. Back then, the U.S. Congress created it to cover federal courts in California, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, and Washington.
How the Circuit Grew
As more states and territories joined the United States, many in the West became part of the 9th Circuit.
- In 1900, the Territory of Hawaii was added.
- In 1912, Arizona joined when it became a state.
- In 1948, the Territory of Alaska was included.
- In 1951, Guam became part of the circuit.
- In 1977, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands was added.
This growth in both people and land is why the 9th Circuit is so large today.
Unique Cases and Challenges
The 9th Circuit covers a very diverse area. This means the judges deal with many different kinds of legal issues. For example, cases from big cities like Los Angeles might be very different from cases in rural Alaska.
One judge, Andrew J. Kleinfeld, who works in Fairbanks, Alaska, once wrote about how different the laws can be. He noted that it's easy to make mistakes when you're not used to certain types of laws. This shows the challenge of having such a large and varied area under one court.
Images for kids




