Viburnum prunifolium facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Viburnum prunifolium |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Foliage | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Dipsacales |
| Family: | Adoxaceae |
| Genus: | Viburnum |
| Species: |
V. prunifolium
|
| Binomial name | |
| Viburnum prunifolium |
|
 |
|
| Natural range | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
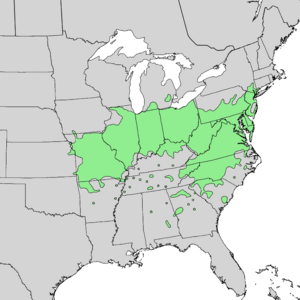
The Viburnum prunifolium is a plant known by many names. People often call it blackhaw or black haw. Other names include blackhaw viburnum, sweet haw, and stag bush. This plant is native to eastern North America. You can find it from Connecticut in the east to eastern Kansas in the west. It also grows south to Alabama and Texas.
Contents
How Blackhaw Grows
The blackhaw is a type of plant that loses its leaves every year. It can be a shrub or a small tree. It usually grows between 2–9 metres (7–30 ft) tall. In colder northern areas, it stays more like a bush. But in warmer southern areas, it can grow into a small tree.
Its trunk is often short and a bit twisted. The branches spread out wide. The bark on older parts of the plant is reddish-brown and rough. New branches start red, then turn green, and finally become dark brown with a red tint.
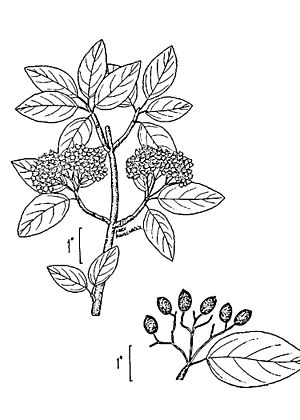
The leaves are simple and can be up to 9 cm long and 6 cm wide. They are oval or round with jagged edges. A red stem, about 1.5 cm long, connects the leaf to the branch. In the fall, these leaves turn a beautiful red color.
What Blackhaw Looks Like
The blackhaw plant has creamy white flowers. Each flower is about 9 mm across. Many flowers grow together in flat-topped clusters. These clusters can be as wide as 10 cm. They bloom in the middle to late spring.
After the flowers, the plant grows fruit. This fruit is a type of drupe, which is like a small plum. Each fruit is about 1 cm long. They are dark blue-black with a powdery coating. The fruits stay on the plant until winter. They become good to eat after they have been frosted. Birds also enjoy eating these fruits.
Blackhaw plants like sunny woodland areas. They need soil that drains water well. They also need enough water to grow strong.
Where Blackhaw is Protected
In the state of Connecticut, the blackhaw plant is considered threatened. This means there are concerns about its numbers there.
How People Use Blackhaw
Blackhaw is a useful plant in many ways. People plant it in gardens because its leaves turn a nice color in the fall. It also provides food for birds in early winter.
This plant has also been used for medicinal purposes for a long time.
Blackhaw as Food
The Meskwaki people eat the fruit of the blackhaw. They eat it raw, and they also cook it to make jam.
Blackhaw for Medicine
For centuries, people have used blackhaw for medicine. It was mainly used for women's health issues. The bark of the plant is the part used in these treatments.
The bark contains special chemicals. Some of these are scopoletin, aesculetin, and salicin. These chemicals are thought to give the plant its medicinal properties.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Viburnum prunifolium para niños
In Spanish: Viburnum prunifolium para niños