Zingiberene facts for kids
Zingiberene is a special natural chemical found mostly in the oil of ginger. It's what gives ginger its unique and spicy smell and taste! This chemical is a type of sesquiterpene, which is a group of natural compounds. It can make up a big part, sometimes up to 30%, of the essential oils found in ginger rhizomes (the underground stems we eat).
How Ginger Makes Zingiberene
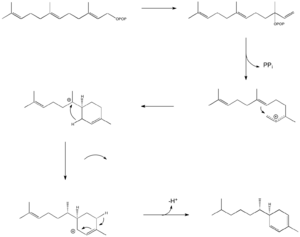
Ginger plants create zingiberene through a natural process inside their cells. This process starts with a molecule called farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP). Think of FPP as a building block.
First, FPP changes its shape to become something called nerolidyl diphosphate. Then, a small part breaks off, and the molecule forms a ring shape. This creates a temporary, unstable spot on the molecule.
Next, a tiny shift happens where a hydrogen atom moves, making the molecule more stable. The final step is when another small part is removed, and a new connection forms, creating the zingiberene molecule.
There's a special helper in this process: an enzyme called Zingiberene synthase. This enzyme is like a tiny worker that helps speed up the reaction, making sure zingiberene and other similar chemicals are formed correctly in the ginger plant.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Zingibereno para niños
In Spanish: Zingibereno para niños