Amorites facts for kids
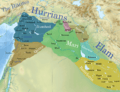
The Amorites were an ancient group of people who came from a region called Syria. They spoke languages that are part of the Semitic languages family, similar to how English and German are part of the Germanic language family.
These people became very important in a large area of southern Mesopotamia (which is modern-day Iraq) between the 21st century BC and the end of the 17th century BC. They were known for setting up many famous city-states, which were like small countries with their own capital city. One of their most famous cities was Babylon, which they helped grow from a small town into a powerful, independent state and a major city.
In ancient texts from Mesopotamia, like those written in Akkadian and Sumerian, the word Amurru was used to describe both the Amorite people and their main god. The Amorites are also mentioned in the Bible as people who lived in Canaan.
Contents
Who Were the Amorites?
The Amorites were a group of people who lived a long, long time ago, starting around 4,000 years ago. They originally came from the western part of the Fertile Crescent, an area that includes modern-day Syria. They were known for their nomadic lifestyle at first, meaning they moved around a lot with their herds.
Their Rise to Power
Over time, the Amorites began to settle down in cities. They moved into Mesopotamia, a land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. This area was already home to other ancient civilizations like the Sumerians and Akkadians. The Amorites gradually gained control of many cities. They established new ruling families in places that were already important centers.
Founding New Kingdoms
The Amorites didn't just take over existing cities; they also founded new kingdoms. They built strong cities and created powerful states. These states often fought with each other for control of land and resources. Their leaders were often strong warriors and clever politicians.
The City of Babylon
One of the most important things the Amorites did was to make Babylon a very powerful city. Before the Amorites, Babylon was just a small, less important town. But under Amorite kings, especially King Hammurabi, Babylon became the center of a huge empire. Hammurabi is famous for creating one of the earliest sets of laws, known as the Code of Hammurabi.
Amorite Culture and Language
The Amorites spoke a Semitic language, which was related to other languages spoken in the ancient Near East. They often adopted the writing systems and some of the customs of the people they lived among, like the Sumerians and Akkadians. This means they used cuneiform writing, which involved pressing wedge-shaped marks into clay tablets.
The End of the Amorite Period
The Amorite period in Mesopotamia lasted for several centuries. However, around the 17th century BC, their power began to decline. Other groups, like the Hittites and the Kassites, started to become more powerful. Eventually, the Amorite kingdoms were replaced by new empires. Even though their rule ended, the Amorites left a lasting mark on the history of the Middle East, especially through cities like Babylon.
Images for kids
-
Destruction of the Army of the Amorites by Gustave Doré.
See also
 In Spanish: Amorreos para niños
In Spanish: Amorreos para niños