Semitic languages facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Semitic |
|
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution: |
Middle East, North Africa, Northeast Africa and Malta |
| Linguistic classification: | Afro-Asiatic
|
| Proto-language: | Proto-Semitic |
| Subdivisions: |
East Semitic (extinct)
|
| ISO 639-2 and 639-5: | sem |
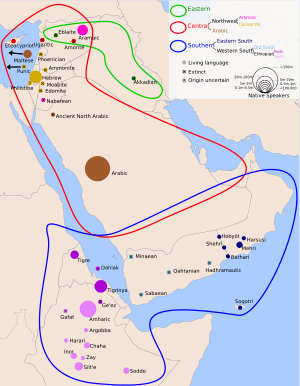 Approximate historical distribution of Semitic languages.
|
|
The Semitic languages are a group of languages spoken by many people around the world. They are part of a larger group called the Afro-Asiatic language family. You can find Semitic languages spoken in places like North Africa, the Middle East, and the Horn of Africa.
More than 470 million people speak Semitic languages today. These languages are also spoken by many people who have moved from these regions to places like North America and Europe. The name "Semitic" comes from Shem, who was a son of Noah in the Bible.
Some well-known Semitic languages include Arabic, Aramaic, and Hebrew.
Contents
What are Semitic Languages?
Semitic languages are a major branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family. This family of languages is believed to have started in the Middle East. Over thousands of years, these languages spread to different parts of the world.
Where are Semitic Languages Spoken?
Today, Semitic languages are mostly spoken in the Middle East, North Africa, and the Horn of Africa. However, because people travel and move, you can hear these languages in many other countries too.
- Middle East: Countries like Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Syria, Israel, and Lebanon.
- North Africa: Countries like Egypt, Sudan, and Algeria.
- Horn of Africa: Countries like Ethiopia and Eritrea.
How Did Semitic Languages Get Their Name?
The name "Semitic" comes from the name of a person called Shem. In the Book of Genesis from the Bible, Shem is one of the sons of Noah. Scholars in the 18th century chose this name to group these languages together.
Examples of Semitic Languages
There are many different Semitic languages, some of which are still spoken today, while others are ancient and no longer used.
Modern Semitic Languages
Many Semitic languages are spoken by millions of people every day.
- Arabic: This is the most widely spoken Semitic language. It is the official language in many countries across the Middle East and North Africa. The Quran, the holy book of Islam, is written in Arabic.
- Hebrew: This language is spoken in Israel. It is an ancient language that was brought back to life in modern times.
- Amharic: This is the official language of Ethiopia.
- Tigrinya: This language is spoken in Eritrea and parts of Ethiopia.
- Maltese: This is the national language of Malta. It is the only Semitic language written using the Latin alphabet.
Ancient Semitic Languages
Some Semitic languages were spoken long ago but are now extinct, meaning they are no longer used.
- Akkadian: This was an important language in ancient Mesopotamia. It was used by the Babylonians and Assyrians. Many ancient texts, like the Epic of Gilgamesh, were written in Akkadian.
- Aramaic: This language was widely spoken in the Middle East thousands of years ago. Parts of the Bible were written in Aramaic. Some small communities still speak different forms of Aramaic today.
- Phoenician: This language was spoken by the Phoenicians, who were famous traders and sailors. They developed an alphabet that influenced many other writing systems.
Key Features of Semitic Languages
Semitic languages have some interesting features that make them different from many other language families.
Root System
One of the most special things about Semitic languages is their "root system." Most words are built from a root of three consonants. Vowels are then added around these consonants to create different words with related meanings.
For example, in Arabic, the root K-T-B (ك-ت-ب) is related to writing:
- Kitāb (كتاب) means "book."
- Kātib (كاتب) means "writer."
- Maktab (مكتب) means "office" or "desk."
This system helps speakers understand the core meaning of words even if they haven't heard the exact word before.
Writing Systems
Many Semitic languages use writing systems where only consonants are written down. Readers usually know which vowels to add based on the context.
- Arabic script: Used for Arabic and some other languages. It is written from right to left.
- Hebrew script: Used for Hebrew. Also written from right to left.
- Ge'ez script: Used for Amharic and Tigrinya. It is written from left to right and includes symbols for both consonants and vowels.
Images for kids
-
Epic of Gilgamesh, an epic poem from ancient Mesopotamia, regarded as the earliest surviving notable literature, written in Akkadian.
-
Map of the Arabic language
See also
 In Spanish: Lenguas semíticas para niños
In Spanish: Lenguas semíticas para niños