Phoenician language facts for kids
Phoenician was an ancient language spoken by the people called Phoenicians. They lived along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in a region known as "Canaan." This area is now parts of countries like Lebanon, Syria, Palestine, northern Israel, and Cyprus. The ancient Egyptians called this land "Pūt."
Phoenician is a Semitic language, which means it belongs to a family of languages that includes Hebrew and Arabic. It was closely related to Hebrew but had its own unique features.
Contents
What is the Phoenician Language?
The Phoenician language was spoken for a very long time, from around the 10th century to the 1st century BC. Experts divide its history into three main periods:
- Archaic Phoenician: From the 10th to the 7th century BC.
- Middle Phoenician: From the 6th to the 4th century BC.
- Late Phoenician: From the 3rd to the 1st century BC.
The name "Phoenicia" comes from the ancient Greeks, who noticed the Phoenicians were famous for making a special purple cloth. The word "Phoenicia" itself is linked to the Greek word for this purple color.
Where Was Phoenician Spoken?
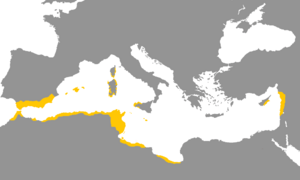
Besides its homeland in the Middle East, Phoenician was also spoken in many other places. The Phoenicians were great sailors and traders, and they set up many colonies across the Mediterranean.
You could hear Phoenician in:
- Modern-day Tunisia, Morocco, and Algeria.
- Islands like Malta, western Sicily, Sardinia, and Corsica.
- The southernmost part of Spain.
In some nearby areas of Anatolia (modern-day Turkey), Phoenician was even used as a very important or "prestige" language.
The Phoenician Alphabet
One of the most important things the Phoenicians gave to the world was their Phoenician alphabet. They were one of the first societies to widely use an alphabet. This alphabet is considered the oldest confirmed consonantal alphabet, also known as an abjad. This means it mostly had letters for consonant sounds, and people had to figure out the vowel sounds from context.
The Phoenician alphabet was incredibly important because it influenced many other writing systems, including the Greek alphabet, which then led to the Latin alphabet that we use today for English!
See also
 In Spanish: Idioma fenicio para niños
In Spanish: Idioma fenicio para niños